Question: The question I would like you to write a memo on is: Write a memo to the Manager of Job 277100 in Marshal Devices (problem
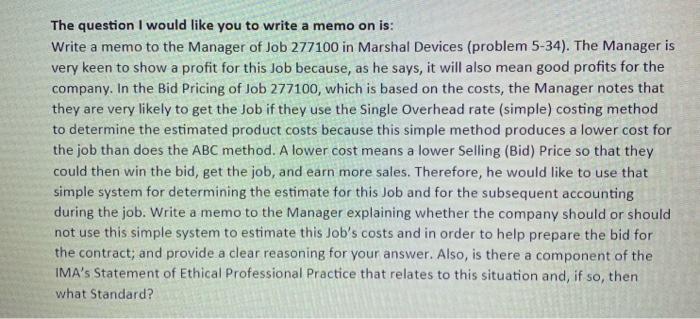
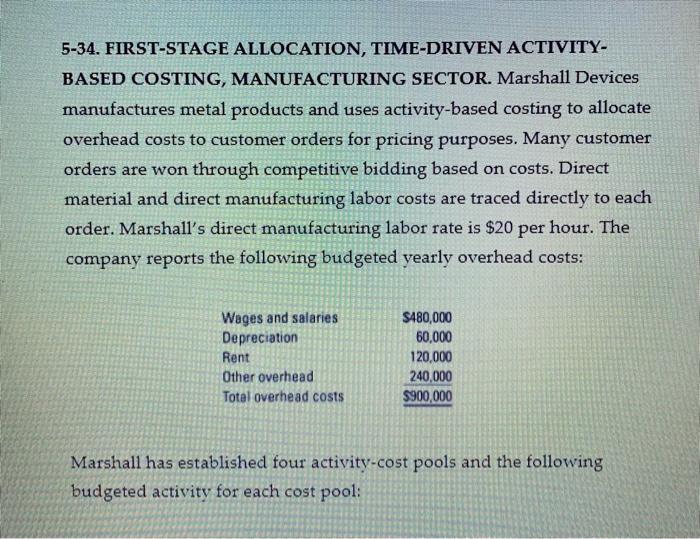

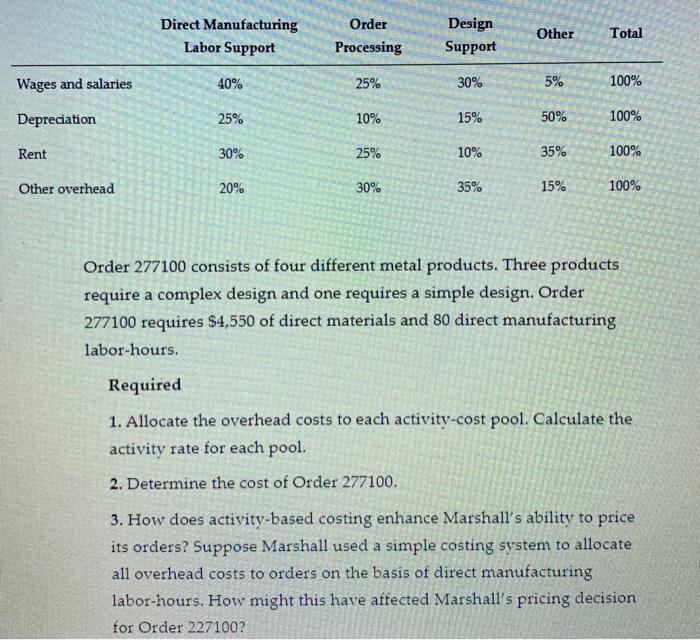

The question I would like you to write a memo on is: Write a memo to the Manager of Job 277100 in Marshal Devices (problem 5-34). The Manager is very keen to show a profit for this job because, as he says, it will also mean good profits for the company. In the Bid Pricing of Job 277100, which is based on the costs, the Manager notes that they are very likely to get the job if they use the Single Overhead rate (simple) costing method to determine the estimated product costs because this simple method produces a lower cost for the job than does the ABC method. A lower cost means a lower Selling (Bid) Price so that they could then win the bid, get the job, and earn more sales. Therefore, he would like to use that simple system for determining the estimate for this Job and for the subsequent accounting during the job. Write a memo to the Manager explaining whether the company should or should not use this simple system to estimate this Job's costs and in order to help prepare the bid for the contract; and provide a clear reasoning for your answer. Also, is there a component of the IMA's Statement of Ethical Professional Practice that relates to this situation and, if so, then what Standard? 5-34. FIRST-STAGE ALLOCATION, TIME-DRIVEN ACTIVITY- BASED COSTING, MANUFACTURING SECTOR. Marshall Devices manufactures metal products and uses activity-based costing to allocate overhead costs to customer orders for pricing purposes. Many customer orders are won through competitive bidding based on costs. Direct material and direct manufacturing labor costs are traced directly to each order. Marshall's direct manufacturing labor rate is $20 per hour. The company reports the following budgeted yearly overhead costs: Wages and salaries Depreciation Rent Other overhead Total overhead costs S480,000 60,000 120,000 240,000 $900,000 Marshall has established four activity-cost pools and the following budgeted activity for each cost pool: Activity-Cost Pool Activity Measure Budgeted Total Activity for the Year Direct manufacturing labor support Number of direct manufacturing labor-hours 30,000 direct manufacturing labor-hours Order processing Number of customer orders 500 orders Design support Number of custom design- hours 2,490 custom design-hours Other Facility-sustaining costs allocated to orders based on direct manufacturing labor- hours 30,000 direct manufacturing labor-hours Some customer orders require more complex designs, while others need simple designs. Marshall estimates that it will do 120 complex designs during a year, which will each take 11.75 hours for a total of 1,410 design-hours. It estimates it will do 180 simple designs, which will each take 6 hours for a total of 1,080 design-hours. Paul Napoli, Marshall's controller, has prepared the following estimates for distribution of the overhead costs across the four activity-cost pools: Direct Manufacturing Labor Support Order Processing Design Support Other Total Wages and salaries 40% 25% 30% 5% 100% Depreciation 25% 10% 15% 50% 100% Rent 30% 25% 10% 35% 100% Other overhead 20% 30% 35% 15% 100% Order 277100 consists of four different metal products. Three products require a complex design and one requires a simple design. Order 277100 requires $4,550 of direct materials and 80 direct manufacturing labor-hours. Required 1. Allocate the overhead costs to each activity-cost pool. Calculate the activity rate for each pool. 2. Determine the cost of Order 277100. 3. How does activity-based costing enhance Marshall's ability to price its orders? Suppose Marshall used a simple costing system to allocate all overhead costs to orders on the basis of direct manufacturing labor-hours. How might this have affected Marshall's pricing decision for Order 227100? 4. When designing its activity-based costing system, Marshall uses time-driven activity-based costing (TDABC) for its design department. What does this approach allow Marshall to do? How would the cost of Order 277100 have been different if Marshall had used the number of customer designs rather than the number of custom design-hours to allocate costs to different customer orders? Which cost driver do you prefer for design support? Why
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


