Question: The three-color problem accepts a graph and returns whether it is possible to color each vertex one of 3 different colors so that no adjacent
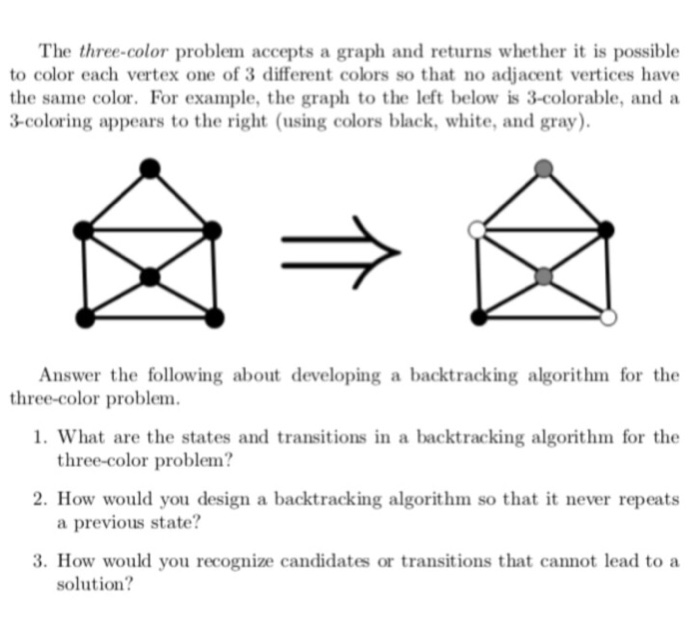
The three-color problem accepts a graph and returns whether it is possible to color each vertex one of 3 different colors so that no adjacent vertices have the same color. For example, the graph to the left below is 3-colorable, and a 3-coloring appears to the right (using colors black, white, and gray Answer the following about developing a backtracking algorithm for the three-color problem. 1. What are the states and transitions in a backtracking algorithm for the three-color problem? 2. How would you design a backtracking algorithm so that it never repeats a previous state? 3. How would you recognize candidates or transitions that cannot lead to a solution
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


