Question: this is an example and the other picture is the actual problem i need help with all the parts i am really confused thank you
this is an example and the other picture is the actual problem i need help with all the parts i am really confused thank you 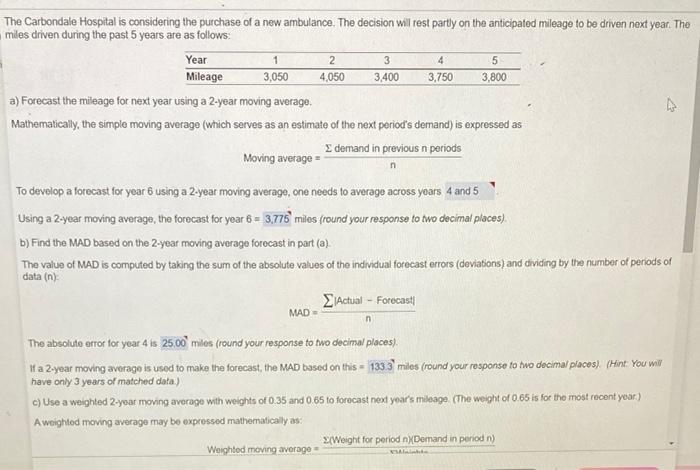

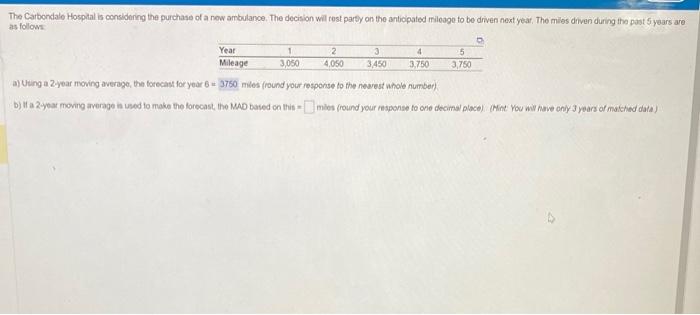
The Carbondale Hospital is considering the purchase of a new ambulance. The decision will rest partly on the anticipated mileage to be driven next year. The miles driven during the past 5 years are as follows: a) Forecast the mileage for next year using a 2-year moving average. Mathematically, the simple moving average (which serves as an estimate of the next period's demand) is expressed as Moving average =ndemandinpreviousnperiods To develop a forecast for year 6 using a 2 -year moving average, one needs to average across yoars Using a 2-year moving average, the forecast for year 6=3.775 miles (round your response to two decimal places). b) Find the MAD based on the 2-year moving average forecast in part (a). The value of MAD is computed by taking the sum of the absolute values of the individual forecast errors (deviations) and dividing by the number of periods of data (n) : MAD=nActualForecast The absolute error for year 4 is 25.00 miles (round your fesponse to two decimal places). If a 2-year moving average is used to make the forecast, the MAD bssed on this = miles (round your response to two decimar places). (Hint: You will have only 3 years of matched data.) c) Use a weighted 2 -year moving average with weights of 0.35 and 0.65 to forocast next yoar's mileage. (The weight of 0.65 is for the most recent year.) A woighted moving average may be expressed mathemalicaly as: Weightedmovingaverage=WWeights(Weightforperiodn)(Demandinperiodn) rr the next year's mileage, the weighted 2-year moving average is 0.353,750+0.6573,800 (round your responses to two decimal places). herefore, the forecast for year 6 is miles (round your response to two decimal places). Vhat MAD results from using this approach to forecasting? The MAD for the forecast developed using a weighted 2-year moving average with weights of 0.35 and 0.65= miles (round your response to two decimal places). (Hint: You will have only 3 years of matched data.) d) Compute the forecast for year 6 using exponential smoothing. an initial forecast for year 1 of 3,000 miles, and =0.30. The basic exponential smoothing formula can be expressed as follows: F1=F11+(A11Ft1) Where Ft is the new forecast, Ft1 is the provious period's forecast, a is the smoothing (or weighting) constant between 0 and 1 , A11 is the proviout periods actual demand. Using exponental smoothing with =0.30 and a starting forecast for year 1 being 3,050 , the forecast developed for years 2 through 4 will be: Year 2=3,050.00 Year 3=3,350.00 Year 4=3,365.00 The Year 5 forecast will be calculated as 3,385,00+0.30(3,7503,3,5.00)=3,480.50 miles (round your responses fo mo decima/ places). Using exponential smoothing with a=0.30 and the forecast for yoar 1 being 3,050 , the forecast for year 6= miles (round your response to wo decimal a) Uing a 2 year moving averago, the forecast for yedr 6 = miles (round your respense to the nearest anole numberf. b) if a 2 syea moving a werage in used to make the lorecast, the MAD based on this = mies (round your fesponse fo orie decimal place) (Mint You wil have onjy 3 years of matehed data?) 


Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


