Question: This is an example of a problem in the course book where the answer has already been provided. Can you please explain how they solved
This is an example of a problem in the course book where the answer has already been provided. Can you please explain how they solved for P(0), P(1), and P(2)? Can you please break down the problem so I can understand the steps? This was solved using the Waiting Line Approach for Arrivals with Formula. 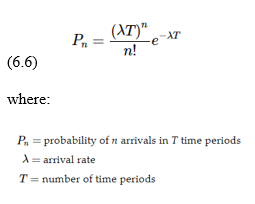

Pn=n!(T)neT where: Pn= probability of n arrivals in T time periods = arrival rate T= number of time periods Customers arrive at a drive-up window at a rate of three per minute (=3). If the number of arrivals follows a Poisson distribution, what is the probability that two or fewer customers would arrive in 1 minute? The probability of two or fewer customers is actually the probability of no arrivals plus the probability of one arrival plus the probability of two arrivals, or: P(2)=P(0)+P(1)+P(2)=0.050+0.149+0.224=0.423,or42.3%
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


