Question: This is coded in MATLAB. Please provide code for part B. Exercise 3 A magic square is a nxn matrix composed of distinct positive integers
This is coded in MATLAB. Please provide code for part B.
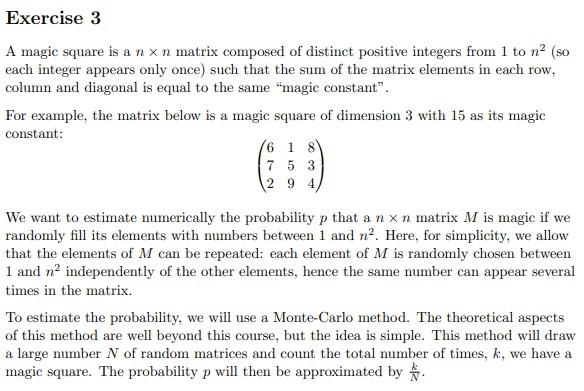

Exercise 3 A magic square is a nxn matrix composed of distinct positive integers from 1 to n (SO each integer appears only once) such that the sum of the matrix elements in each row, column and diagonal is equal to the same "magic constant". For example, the matrix below is a magic square of dimension 3 with 15 as its magic constant: 16 1 8 7 5 3 (2 9 4) We want to estimate numerically the probability p that a nxn matrix M is magic if we randomly fill its elements with numbers between 1 and n. Here, for simplicity, we allow that the elements of M can be repeated: each element of M is randomly chosen between 1 and n independently of the other elements, hence the same number can appear several times in the matrix. To estimate the probability, we will use a Monte-Carlo method. The theoretical aspects of this method are well beyond this course, but the idea is simple. This method will draw a large number N of random matrices and count the total number of times, k, we have a magic square. The probability p will then be approximated by b) Write a function named randomMatrix(n) that returns a nxn matrix with its elements that are integers randomly chosen between 1 and na. Hints: As a reminder, the built-in MATLAB function rand (n) generates a nxn matrix whose elements are real numbers (i.e., double) uniformly distributed between 0 and 1. Generating numbers uniformly distributed between 0 and a can simply be achieved by calling a * rand (n). As a reminder, a double number x can be converted to an unsigned integer using, for example, the MATLAB built-in functions uint16(x). See Lecture 2 and in particular its associated script lect_02.m
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


