Question: This just means translating the formula above (21GR2Mt2) into Python code. You'll have to replace each variable in the math formula with the name we
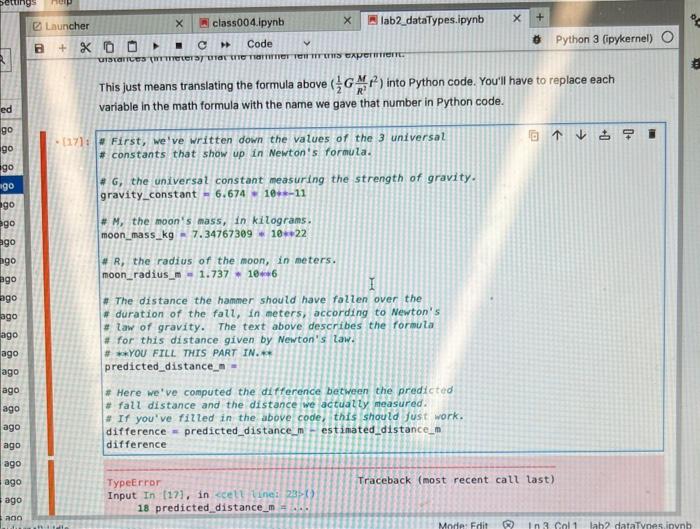
This just means translating the formula above (21GR2Mt2) into Python code. You'll have to replace each variable in the math formula with the name we gave that number in Python code. - First, we've written down the values of the 3 universal * constants that show up in Newton's formula. * G, the universal constant measuring the strength of gravity. gravity_constant =6.674=10+k11 * M, the moon's mass, in kilograns. moon_mass_kg =7.34767309=10+22 * R, the radius of the moon, in meters. moon_radius_m = =1.737186 7. The distance the hammer should have fallen over the * duration of the fall, in neters, according to Newton's 3. Law of gravity. The text above describes the formula A. for this distance given by Newton's law. * w*YOU FILL. THIS PART IN.** predicted_distance_m = * Here we've computed the difference between the predicted * fall distance and the distance we actually measured. * If you've fitted in the above code, this should just work. difference = predicted_distance m - estimated_distance_m difference
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


