Question: This lab has been confusing me and i cannot seem to come to a solution that works on my end, my program keeps erroring out
This lab has been confusing me and i cannot seem to come to a solution that works on my end, my program keeps erroring out so i would like to see how it would be done to learn and apply in my own way.
- Using NetBeans 12, write a Java program (called Lab04) consisting of two classes called Main and MyArrayUtility.
- The Main class looks like this:
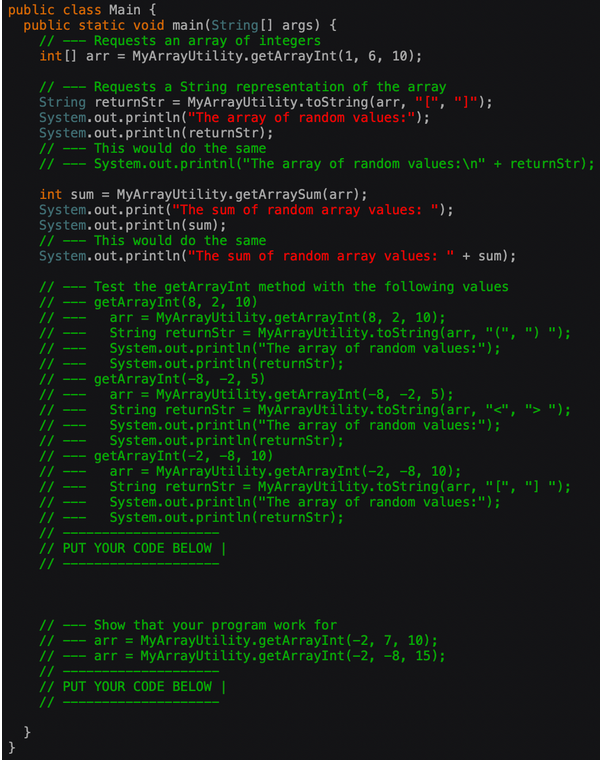
- MyArrayUtility class has the following methods:
- [25 points] public static int[] getArrayInt(int minVal, int maxVal, int numValues)
- This method returns an array of random integers between minVal and maxVal, inclusive. The length of the array is numValues. So, if someone called the following method
- int[] arr = MyArrayUtility.getArrayInt(1, 6, 10)
- then the variable arr would contain an array of ten random numbers between 1 and 6, inclusive. Here is an example of random values returned in an array: 1,4,1,2,4,3,1,3,5,3
- Verify that this works for values negative values of
- This method returns an array of random integers between minVal and maxVal, inclusive. The length of the array is numValues. So, if someone called the following method
- [25 points] public static String toString(int[] arr, String strLeft, String strRight)
- This method returns a string representation of an array of integers. Therefore, if someone called the following method
- String returnStr = MyArrayUtility.toString(arr, "[", "]")
- the returnStr would contain a string representation of the array that looks something like this
- [1][4][1][2][4][3][1][3][5][3]
- If you used "" as parameters, a string such as the one below would be returned
- Neat, right?
- This method returns a string representation of an array of integers. Therefore, if someone called the following method
- [25 points] public static int getArraySum(int[] arr)
- This method returns an integer representing the sum of all values in array arr.
- Note that you will use a for-loop to iterate through entire array, adding each array value (arr[i]) to the sum of values.
- [15 points] Make your getArrayInt method fool-proof. Meaning, check that the values passed are correct, such as that the maxVal is greater than minVal (how does this work when dealing with negative minVal and negative maxVal? If the parameters are not correctly ordered (minVal > maxVal), fix it in your code by swapping the minVal and maxVal. Think about what happens when both minVal and maxVal are negative values. Analyze this before you begin coding. Your program will be tested by exposing it to method calls such as
- getArrayInt(8, 2, 10)
- getArrayInt(-8, -2, 5)
- getArrayInt(-2, -8, 10)
- [10 points] Show in the main method of the Main class that your getArrayInt method from above works for the following examples. In other words, show that the method generates correct values. Run your program several times, making sure that the output is correct.
- getArrayInt(-2, 7, 10)
- getArrayInt(-2, -8, 15)
public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { Requests an array of integers int[] arr = MyArrayUtility.getArrayInt(1, 6, 10); // Requests a String representation of the array String returnStr = MyArrayutility.toString(arr, "[", "1"); System.out.println("The array of random values:"); System.out.println(returnStr); This would do the same // System.out.printnl("The array of random values: " + returnStr); int sum = MyArrayUtility.getArraySum(arr); System.out.print("The sum of random array values: "); System.out.println( sum); // -- This would do the same System.out.println("The sum of random array values: + sum); Test the getArrayInt method with the following values getArrayInt(8, 2, 10) arr = MyArrayutility.getArrayInt(8, 2, 10); String returnStr = MyArrayUtility.toString(arr, "(", ") "); System.out.println("The array of random values:"); System.out.println(returnStr); getArrayInt(-8, -2, 5) MyArrayUtility.getArrayInt(-8, -2, 5); String returnStr = MyArrayUtility.toString(arr, " "); System.out.println("The array of random values:"); System.out.println(returnStr); getArrayInt(-2, -8, 10) MyArrayUtility.getArrayInt(-2, -8, 10); String returnStr = MyArrayUtility.toString(arr, "[", "] "); System.out.println("The array of random values:"); // System.out.println(returnStr); arr = arr = // PUT YOUR CODE BELOW | Show that your program work for arr = MyArrayUtility.getArrayInt(-2, 7, 10); MyArrayUtility.getArrayInt(-2, -8, 15); arr = // PUT YOUR CODE BELOW | }
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


