Question: This problem relates to oxy-fuel combustion - when a hydrocarbon fuel is burned in pure oxygen and the products consist of only carbon dioxide and
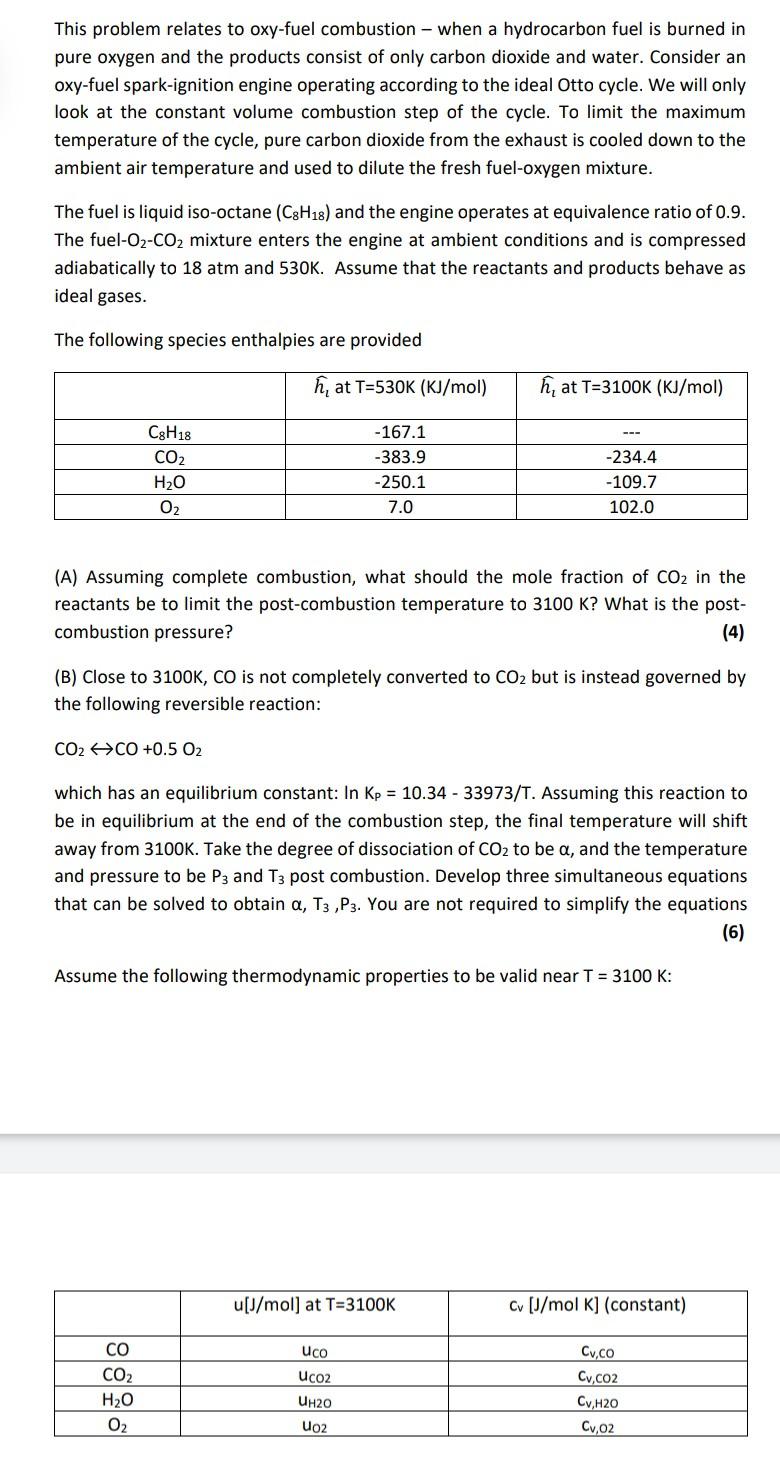
This problem relates to oxy-fuel combustion - when a hydrocarbon fuel is burned in pure oxygen and the products consist of only carbon dioxide and water. Consider an oxy-fuel spark-ignition engine operating according to the ideal Otto cycle. We will only look at the constant volume combustion step of the cycle. To limit the maximum temperature of the cycle, pure carbon dioxide from the exhaust is cooled down to the ambient air temperature and used to dilute the fresh fuel-oxygen mixture. The fuel is liquid iso-octane (C3H18) and the engine operates at equivalence ratio of 0.9. The fuel-O2-CO2 mixture enters the engine at ambient conditions and is compressed adiabatically to 18 atm and 530K. Assume that the reactants and products behave as ideal gases. The following species enthalpies are provided h, at T=530K (KJ/mol) h, at T=3100K (KJ/mol) C8H18 CO2 H2O O2 -167.1 -383.9 -250.1 7.0 -234.4 -109.7 102.0 (A) Assuming complete combustion, what should the mole fraction of CO2 in the reactants be to limit the post-combustion temperature to 3100 K? What is the post- combustion pressure? (4) (B) Close to 3100K, CO is not completely converted to CO2 but is instead governed by the following reversible reaction: CO2 CO +0.5 02 which has an equilibrium constant: In Kp = 10.34 - 33973/T. Assuming this reaction to be in equilibrium at the end of the combustion step, the final temperature will shift away from 3100K. Take the degree of dissociation of CO2 to be a, and the temperature and pressure to be P3 and T3 post combustion. Develop three simultaneous equations that can be solved to obtain a, T3 ,P3. You are not required to simplify the equations (6) Assume the following thermodynamic properties to be valid near T = 3100 K: u[J/mol] at T=3100K Cv [J/mol K] (constant) uco Ucoz CO CO2 H20 02 Cv.co Cv.co2 CyH2O Cv.cz UH2O Uo2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


