Question: Use Python to complete the following code. 3. Classification and K Nearest Neighbor Download and read the document that explains how to apply the K
Use Python to complete the following code.
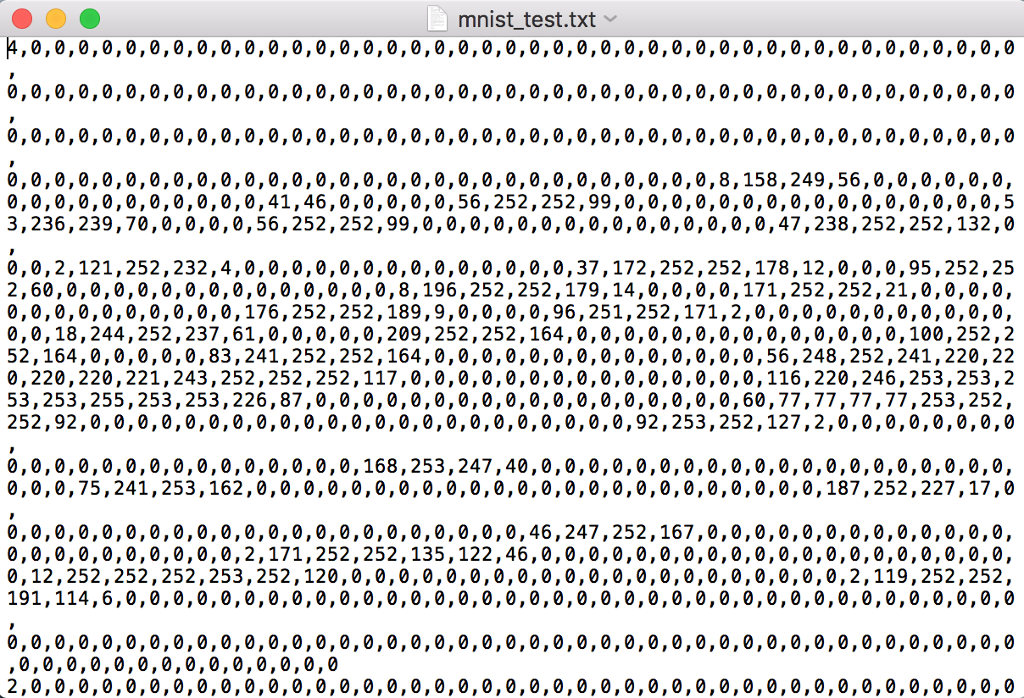

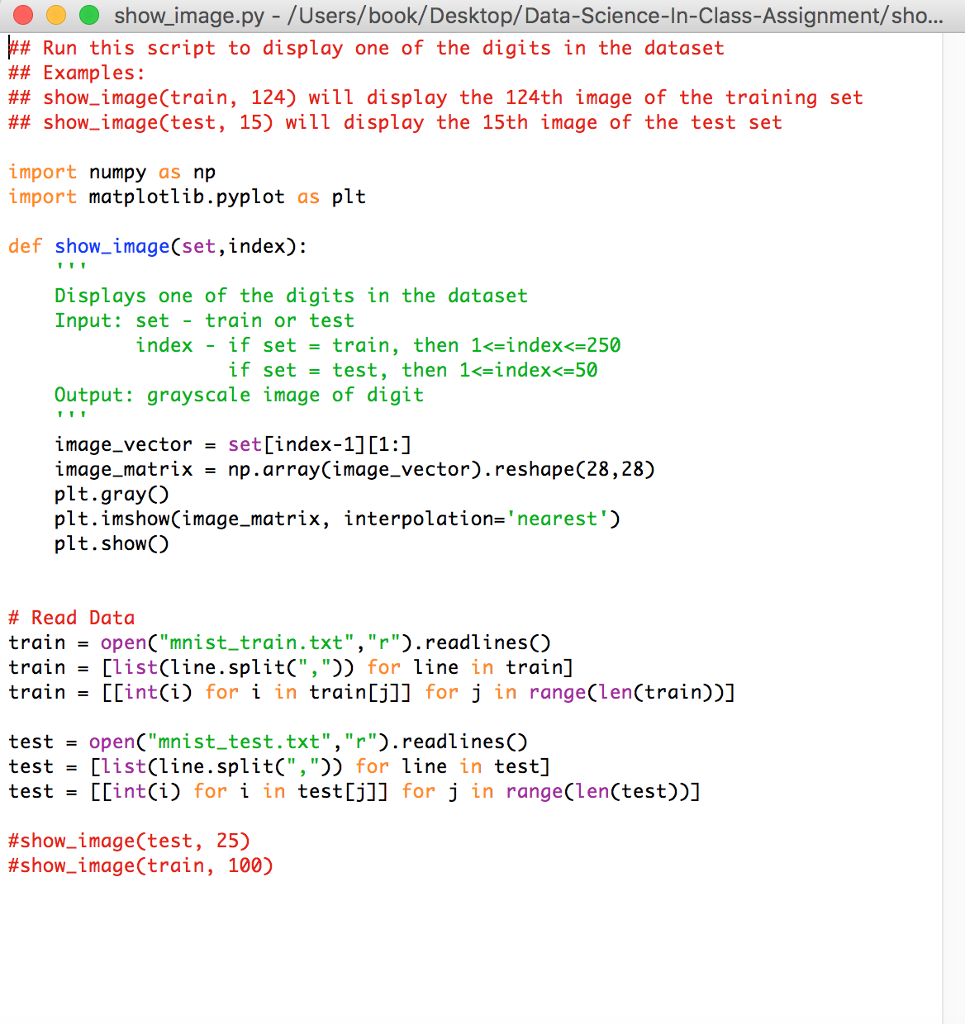
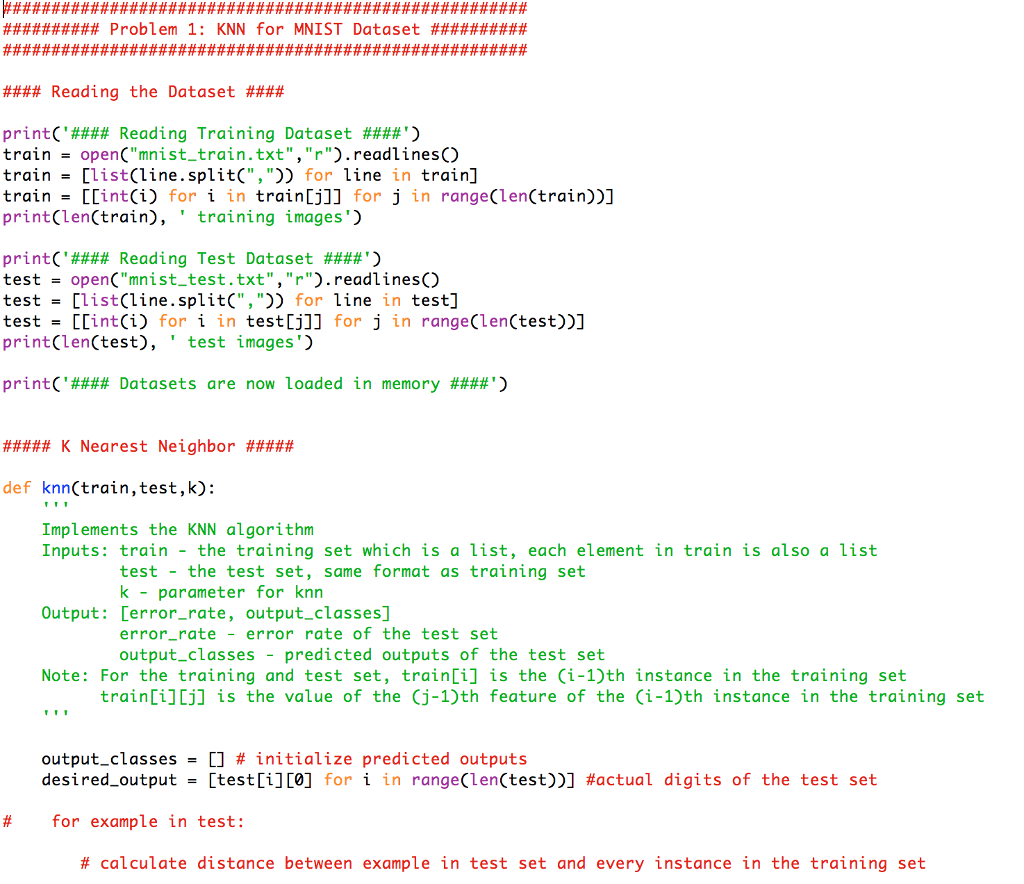
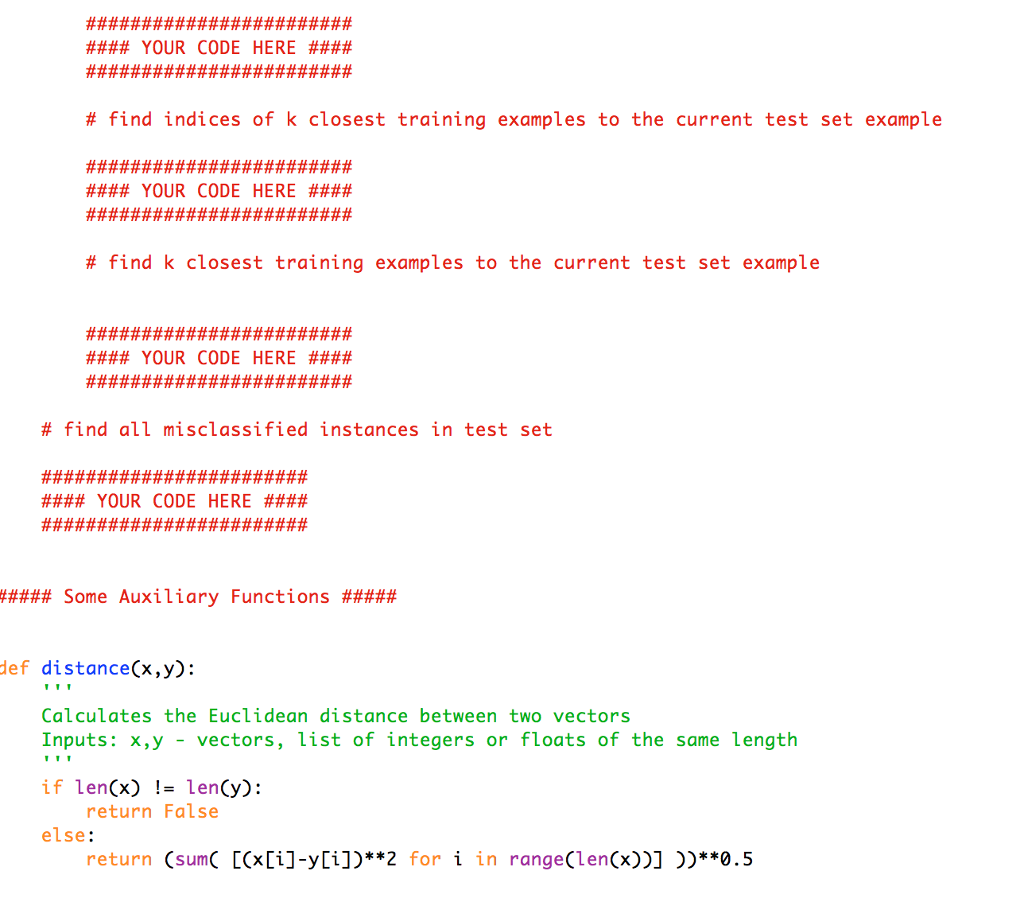
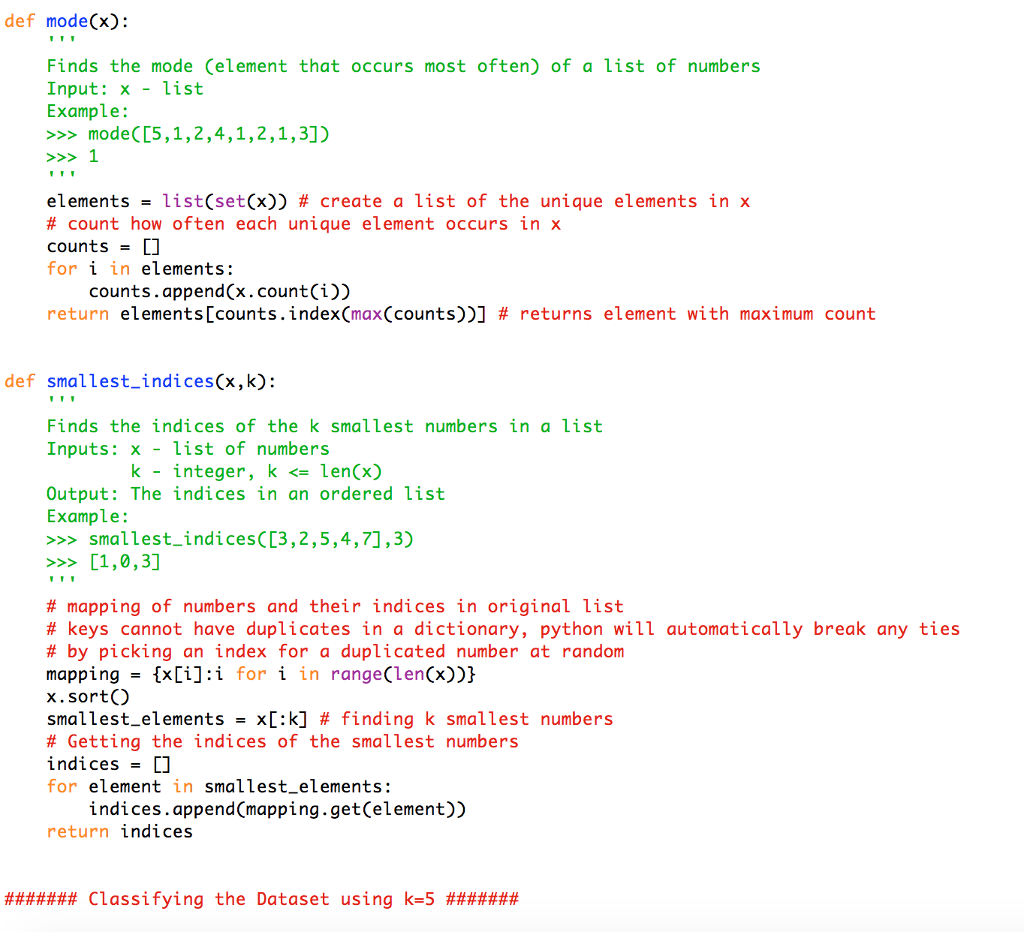
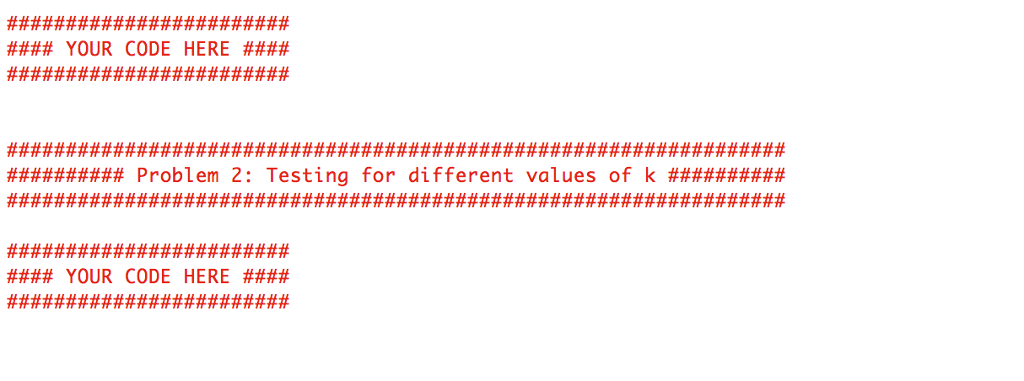
3. Classification and K Nearest Neighbor Download and read the document that explains how to apply the K Nearest Neighbor (KNN) algorithm to classify data. You are going to use KNN to automatically identify single-digit integers in fuzzy images of handwriten digits; the US postal service uses a similar optical character recognition (OCR) of zip codes to automatically route letters to their destination. The MNIST dataset is a database of such handwritten digits. The original dataset can be downloaded at http:/lyann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist, For this problem, we randomly chose a subset of the original dataset. We have provided you with two data files, mnist train.txt, mnist test.txt, which consists of a training set containing 250 digits, and a test set 50 digits. Your job will be to try to classify all the images in the test set using KNN and compare your results with the original digits. Each line in both the training and test set represents an image of size 28 x 28 by a vector of length 784, with each feature specifying a grayscale pixel value. The first column contains the labels of the digits, 0-9, the next 28 columns represent the first row of the image, and so on. We also provide a script written in Python, show image.py to show a single image; using this script will help you have a better understanding of what the data looks like and how it is represented You are expected to do the following: I, Using KNN, classify all the images in the test set setting k 5, Calculate the error rate, which is defined as (Number of misclassified data points in the test set) (Total number of data points in the test set) ork. Setting k I will classify every new data in the class of its closest neighbor whereas setting k = data ed will One of the problems you will encounter when implementing KNN is choosing the appropriate value classify every new point as the most common class in the dataset. 2. Repeat your KNN classification process, this time setting k = 1 , 3, 5, 1 1, 17, 23, 47, and compare the error rates Two larger datasets are available if you want to push the comparison even further: mnist train-big.txt is a training set containing 2000 digits, mnist test-big.txt is a test set with 1000 digits 3. Classification and K Nearest Neighbor Download and read the document that explains how to apply the K Nearest Neighbor (KNN) algorithm to classify data. You are going to use KNN to automatically identify single-digit integers in fuzzy images of handwriten digits; the US postal service uses a similar optical character recognition (OCR) of zip codes to automatically route letters to their destination. The MNIST dataset is a database of such handwritten digits. The original dataset can be downloaded at http:/lyann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist, For this problem, we randomly chose a subset of the original dataset. We have provided you with two data files, mnist train.txt, mnist test.txt, which consists of a training set containing 250 digits, and a test set 50 digits. Your job will be to try to classify all the images in the test set using KNN and compare your results with the original digits. Each line in both the training and test set represents an image of size 28 x 28 by a vector of length 784, with each feature specifying a grayscale pixel value. The first column contains the labels of the digits, 0-9, the next 28 columns represent the first row of the image, and so on. We also provide a script written in Python, show image.py to show a single image; using this script will help you have a better understanding of what the data looks like and how it is represented You are expected to do the following: I, Using KNN, classify all the images in the test set setting k 5, Calculate the error rate, which is defined as (Number of misclassified data points in the test set) (Total number of data points in the test set) ork. Setting k I will classify every new data in the class of its closest neighbor whereas setting k = data ed will One of the problems you will encounter when implementing KNN is choosing the appropriate value classify every new point as the most common class in the dataset. 2. Repeat your KNN classification process, this time setting k = 1 , 3, 5, 1 1, 17, 23, 47, and compare the error rates Two larger datasets are available if you want to push the comparison even further: mnist train-big.txt is a training set containing 2000 digits, mnist test-big.txt is a test set with 1000 digits
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


