Question: Use the Ellingham diagram to answer the questions Continuous reading Auto Scroll Note Background Screen Grab Find Highlight 6. What is the oxygen partial pressure


Use the Ellingham diagram to answer the questions
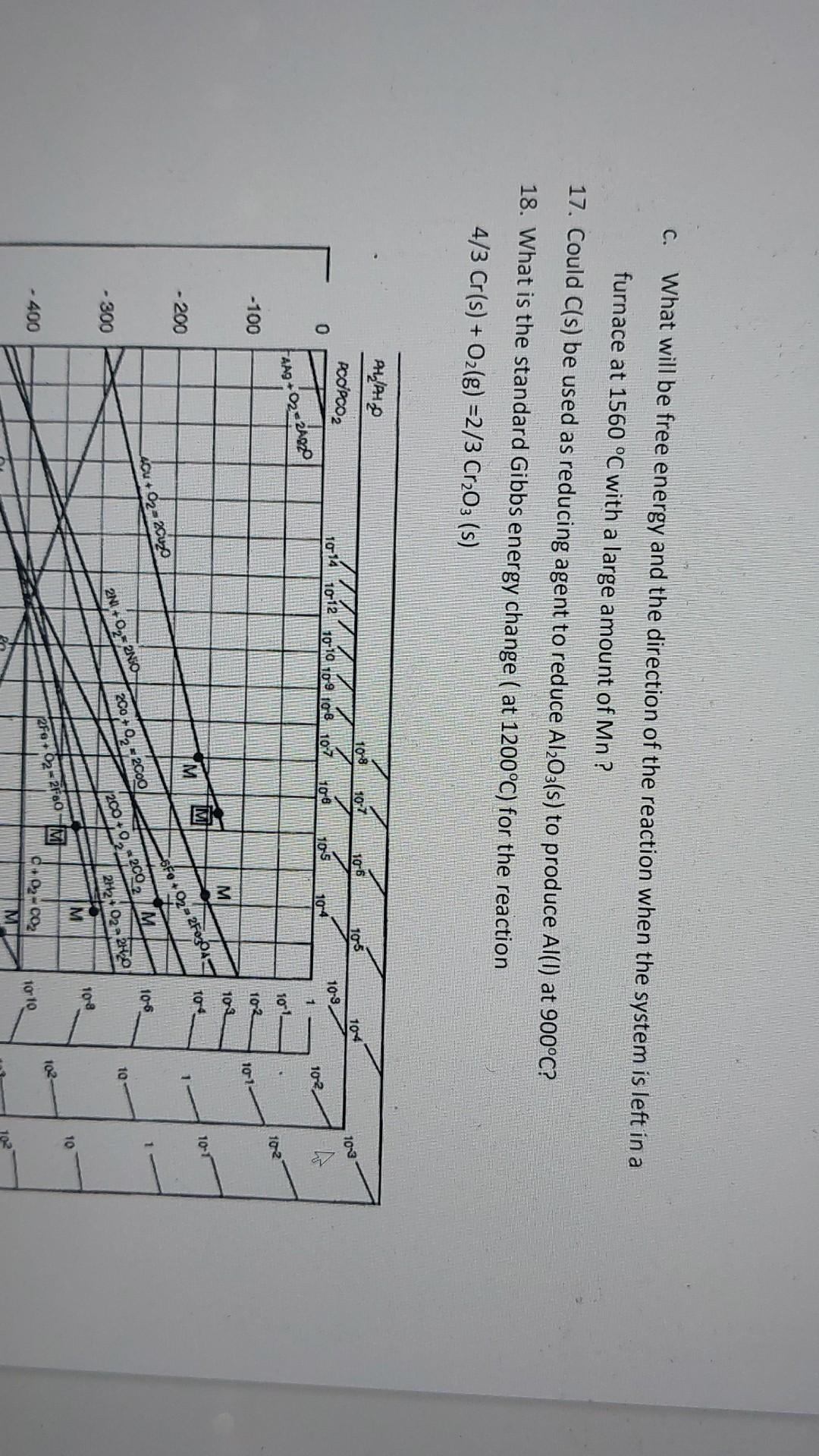
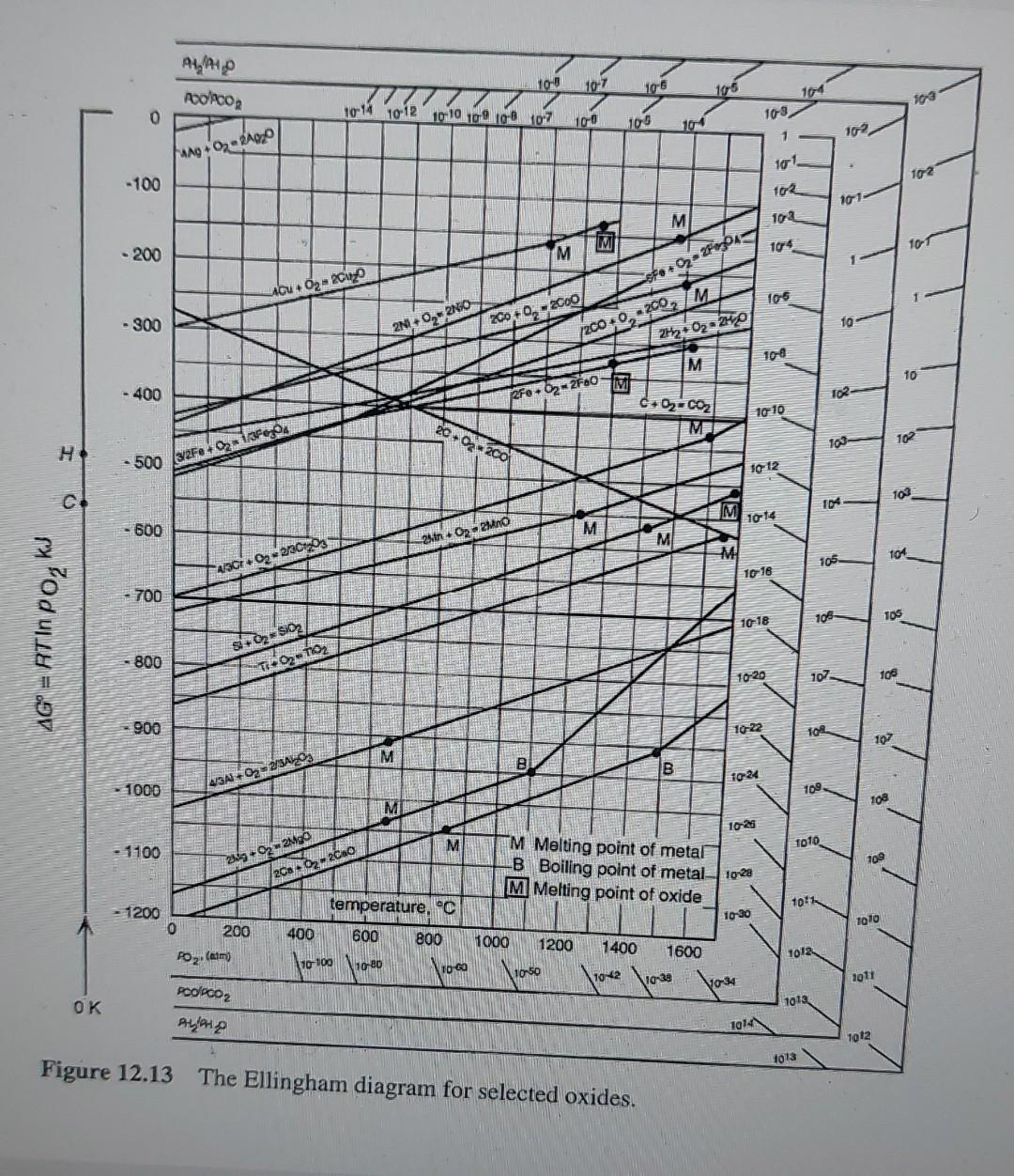
Continuous reading Auto Scroll Note Background Screen Grab Find Highlight 6. What is the oxygen partial pressure that is in equilibrium with Ti and TiO2 at 1500C? 7. What is the highest oxygen partial pressure that is in equilibrium with Mg at room temperature? 8. What is the lowest CO/CO2 pressure ratio that is in equilibrium with Ca at 1400C 9. Which elements can reduce Cr2O3 to Cr at 500C? 10. Which oxides can Co reduce at 1000C? 11. A smelting furnace is run at 1800 C and 10-14 atm partial oxygen pressure to reduce Cr2O3. Engineer in charge of production wants to reduce the temperature to cut electrical costs. How many degrees should furnace temperature be lowered while keeping oxygen pressure constant? 12. What should the temperature of a furnace to reduce Cu O by solid carbon (C+ O2 = 200) be set minimally? How does the reaction quotient k for the overall reduction reaction with increasing temperature? 13. Is Mn stable at an oxygen partial pressure of 10-22 atm and 800 C? If not, what should be wone to obtain Mn at this condition? 14. Will the reaction 2Cu(l) + Oz(g) = Cu2O(s) go spontaneously to the right or to the left at 1500 C when oxygen pressure is 1 atm? 15. At what partial oxygen pressure will above reaction spontaneously go in the other direction? 16 Pure iron and oxygen react accordingly to form Feo: reading Auto Scroll Background Screen Grab Find 12. What should the temperature of a furnace to reduce Cu20 by solid carbon (C+ O2 = 200) be set minimally? How does the reaction quotient K for the overall reduction reaction with increasing temperature? 13. Is Mn stable at an oxygen partial pressure of 10-22 atm and 800 C? If not, what should be done to obtain Mn at this condition? 14. Will the reaction 2 Cu(I) + 12 O2(g) = Cu2O(s) go spontaneously to the right or to the left at 1500 C when oxygen pressure is 1 atm? 15. At what partial oxygen pressure will above reaction spontaneously go in the other direction? 16. Pure iron and oxygen react accordingly to form Feo : 2 Fe(s) + O2(g) 2FeO (s) -> a. Determine the entropy change of the reaction b. Determine the free energy change of the reaction as a function of temperature C. What will be free energy and the direction of the reaction when the system is left in a furnace at 1560 C with a large amount of Mn? 17. Could C(s) be used as reducing agent to reduce Al2O3(s) to produce Al(l) at 900C? 18. What is the standard Gibbs energy change ( at 1200C) for the reaction 4/3 Cr(s) + O2(g) =2/3 Cr203 (s) PH/PHO PCOPCO2 10-8 10-7 106 105 104 1013 1014 1012 10-10 10-9 108 10:7 10-6 0 10-9 10-5 104 1 10-2 FAAg+2=24020 10-1 10_2. -100 102 101 M 10-3 to 4 10-1 M - 200 Fo+ 02-2F0304 4.Cu +62-2Cuzo 10-6 200 +0,- 2000 10 - 300 2N0 +02-2NO 2000-2002 IM 212 02 2H2O 108 M 10 102 20.02 - 400 02-coz torto 4, Po og 110-8 10-7 1106 105 104 0 1914 10 12 10 10 10 109 107 109 100 105 10 102 fang+02 -RADO 101 102 - 100 102 101 M 102 M 104 TOT - 200 M sfo+02-27 Alu + - 2 105 - 300 2000 - 2000 10 2 +0,250 2000, 2002 M 2H2 + O2-20 OVE fo- | 10 - 400 RF.O2-2F60 102 C+02=C02 ME 10010 2007-200 103- 102 H 500 (3/2Fe +18Fores +2 10-12 102 c! 10+ M 10 14 600 M 2. Op. Mno M M 104 105 4/3002213C0g 16 16 700 10-18 105 105 kil AG = RT IN PO, sito sio 800 TOTO 10-20 107 106 900 10-22 104 107 M B 1024 - 1000 A/3A +03 - 2/5AZOS 109 M Toa 10-25 M 1010 - 1100 109 292 290 - F 2000 - 200 M Melting point of metal -B Boiling point of metal 1028 M Melting point of oxide temperature. "C 1011 10-30 foto 1200 0 200 Poz. (am 800 1000 400 600 110100 Noto 1200 1400 1012 1060 10-50 1600 110-28 70-42 2011 No 34 OK POPCO2 ALPHA 1013 1914 1012 1013 Figure 12.13 The Ellingham diagram for selected oxides
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


