Question: Use the following references below to solve a , b , and c using the image to guide the problem. For a reference LWR: assume
Use the following references below to solve ab and c using the image to guide the problem.
For a reference LWR: assume a thermal efficiency is power MWe, uranium is $lb UO SWU is $kgSWU conversion is $kgU fabrication costs are $kgU losses in conversion losses in fabrication tails assay of wt reference core contains tonne fuel with enrichment of An average economical grade of uranium ore is Each fuel assembly contains kg of fuel. The reactor operates on a batch equilibrium cycle of months which includes months at power including day startup and day for shutdown.
Data for recycling and disposal: Price of reprocessing $kg used fuel Price of MOX fabrication $kg Price of DU $kg used fuel is kg used fuelkg fresh fuel, used fuel has g fissile Pukg used fuel, fissile Pu has a reactivity equivalency of g Uequivalentg fPu loss in reprocessing; losses in fabrication same as UO fuel; Table shows information on reactor grade plutonium; dry casks can hold spent fuel assemblies and costs $M to purchase and load.
Financialeconomic data: annual interest rate is interest is compounded monthly
Assume the average home requires an electrical power of kW with only power from nuclear energy. Suppose the average home occupancy is persons and an average life expectancy of years. Utilize data for the reference LWR
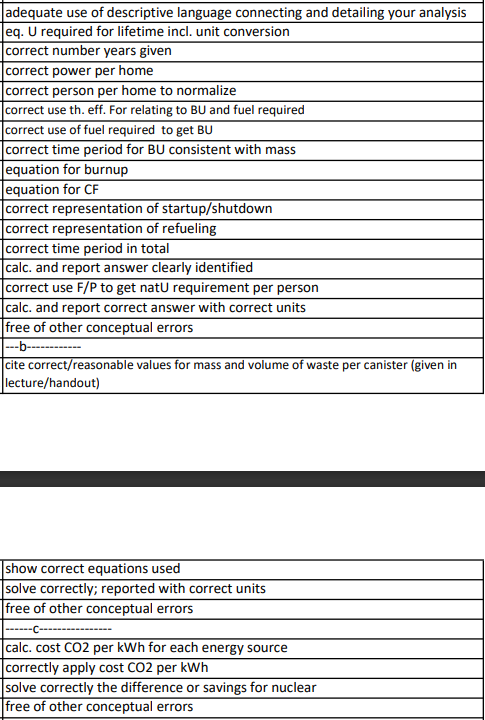
a What would be the lifetime uranium resource requirement per person without recycling?
b What would be the lifetime generation of vitrified highlevel waste HLW per person in kg and liters assuming reprocessing and recycling of U and Pu Recall from your lecture notes and handouts for chapter the vitrified waste containers in France weigh kg and hold the HLW equivalent of recycled fuel assemblies.
c Using the comparison of the life cycle carbon emissions for different technologies in terms of grams Carbon equivalent per kWhe from introductory slides for Chapter and assuming a carbon tax of $t CO what would be the per person lifetime savings in carbon taxes afforded by the referenced nuclear plant per year over an equal production of electricity by coal? By
natural gas? Read average values from below as: Nuclear: gCOeqkWhe read as grams CO equivalent per kWhe Coal: gCOeqkWhe Natural gas: gCOeqkWhe
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


