Question: Uses MATLAB can anyone help with codes for exercises 5 and 6? Thanks! and c2 units vertically. In homogeneous coordinates the translated vector is (1+C1,2

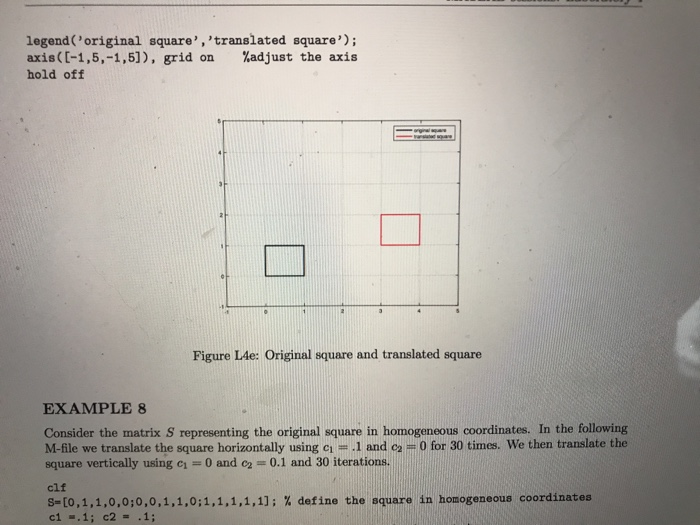

and c2 units vertically. In homogeneous coordinates the translated vector is (1+C1,2 + 2, 1). We need a matrix M such that It is easy to verify that the matrix has the desired property EXAMPLE 7 We will apply a horizontal translation of 3 units and a vertical translation of 1 unit. The matrix that 'accomplishes that is M-10 11 . apply the transformiation to the square S, we will need to 1 convert the square to homogeneous coordinates. This is done by adding a row of ones to the matrix S so that the new matrix is S = | 0 0 1 1 01, we can plot the original square together with the translated version by executing the following commands: 0 1 1 0 0 clf S= [0,1,1,0,0;0,0,1,1,0:1,1,1,1,1); %square in homogeneous coordinates Mr(1,0,3:0, 1, 1:0,0,1); %translation matrix MS-M S; plot (S (1, :),S(2, :),'k' ,'linewidth', 2); %plot the original square in black hold orn plot (MS (I': ), MS (2, :),'r','linewidth',2); % plot the translated square in red % apply the translation to the square
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


