Question: Using Matlab, write a function that is called like this: mbd = spherical_mirror_aberr(fn,D), where all arguments are scalars, fn is the f-number of a concave
Using Matlab, write a function that is called like this: mbd = spherical_mirror_aberr(fn,D), where all arguments are scalars, fn is the f-number of a concave spherical mirror, D is its diameter in millimeters, and mbd is the mean blur diameter in millimeters. The f-number equals the focal length f of the mirror divided by its diameter. Ideally, all the rays of light from a distant object, illustrated by the parallel lines in the figure, would reflect off the mirror and then converge to a single focal point. The magnified view shows what actually happens. The light striking a vertical plane at a distance f from the mirror is spread over a circular disk. The light from the center of the mirror strikes the center of the disk, but light arriving from a point a distance x from the center of the mirror strikes the plane on a circle whose diameter d is equal to 2tan2 ?1, where = sin . The function calculates d for all values of x in the vector x = 0:delta_x:D/2, where delta_x = 0.01. Then it calculates the mean blur diameter using this weighted formula:
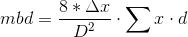
where the sum includes all x(n)d(n), and returns it. Here are three example runs: >> format long
>> mbd = spherical_mirror_aberr(8,152)
mbd = 0.029743954651679
>> mbd = spherical_mirror_aberr(8,300)
mbd = 0.058695642823892
>> mbd = spherical_mirror_aberr(10,300)
mbd = 0.037543964166654
mod 8 Ar D2 mod 8 Ar D2
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


