Question: Using Python 3 Exercise 4: Numeric integration (challenging) Recall from your statistics or econometrics class that the probability density function (pdf) of a normal distribution
Using Python 3
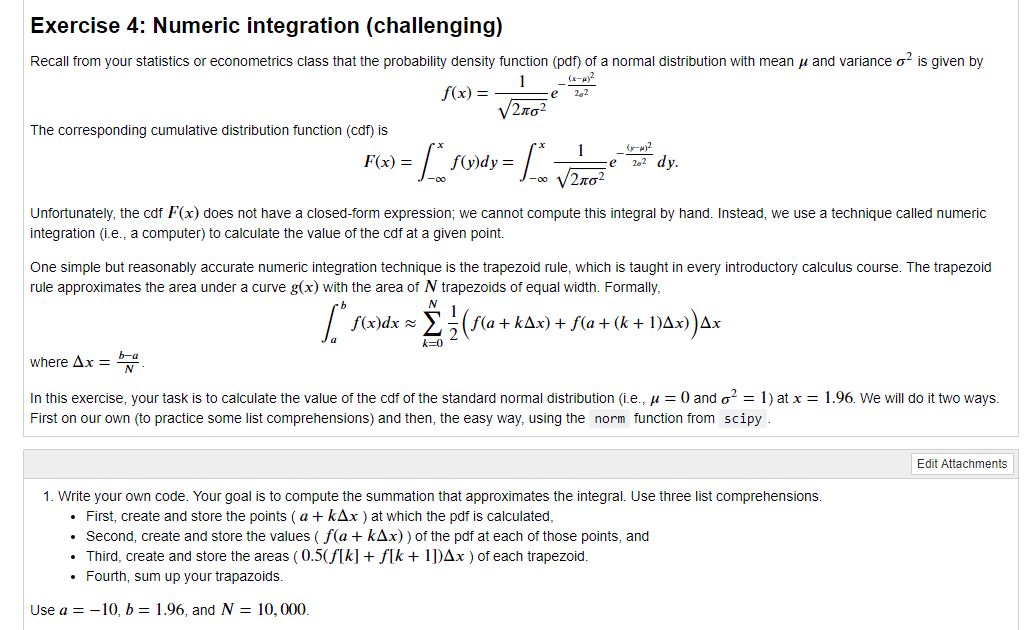
Exercise 4: Numeric integration (challenging) Recall from your statistics or econometrics class that the probability density function (pdf) of a normal distribution with mean n and variance o2 is given by V2702 The corresponding cumulative distribution function (cdf) is F(x) = [swdy = [ Ledy. J-V2102 Unfortunately, the cdf F(x) does not have a closed-form expression; we cannot compute this integral by hand. Instead, we use a technique called numeric integration (ie, a computer) to calculate the value of the cdf at a given point. One simple but reasonably accurate numeric integration technique is the trapezoid rule, which is taught in every introductory calculus course. The trapezoid rule approximates the area under a curve g(x) with the area of N trapezoids of equal width. Formally, | f(x)dx = { }(f(a+kAx) + f(a+(k+ 1)^x))^x where Ax = baca In this exercise, your task is to calculate the value of the cdf of the standard normal distribution (i.e., = 0 and o? = 1) at x = 1.96. We will do it two ways. First on our own (to practice some list comprehensions) and then, the easy way, using the norm function from scipy. Edit Attachments 1. Write your own code. Your goal is to compute the summation that approximates the integral. Use three list comprehensions. First, create and store the points ( a + kAx ) at which the pdf is calculated, . Second, create and store the values (f(a + kAx)) of the pdf at each of those points, and Third, create and store the areas (0.5(f[k] + f[k + 1])Ax ) of each trapezoid. Fourth, sum up your trapazoids. Use a = -10, b = 1.96, and N = 10,000
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


