Question: Using python Problem 3 (3 points) Random Walk theory provides us with the following nice (anf maybe counterintuitive) asymptotic statements: lim C2N LA M2v We
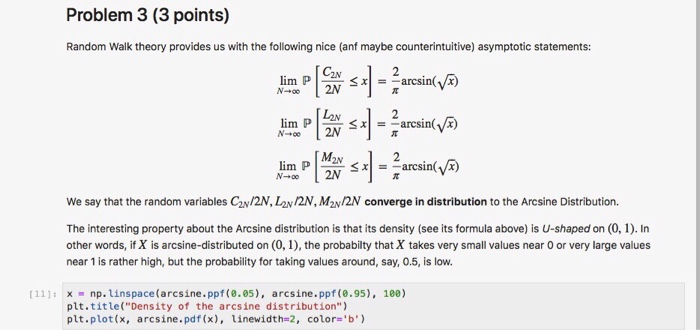
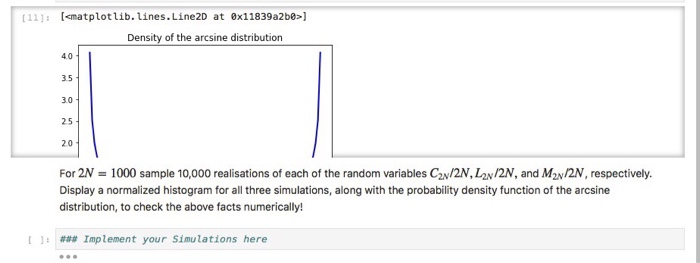
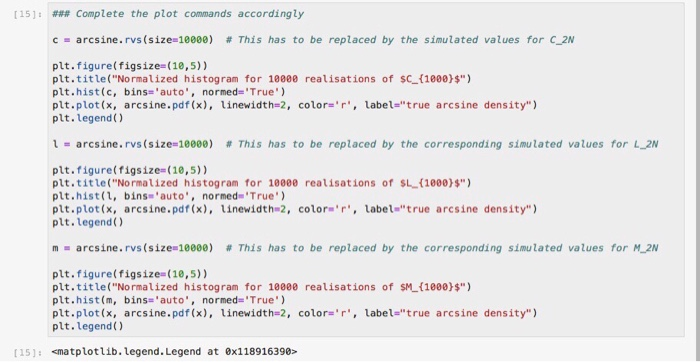
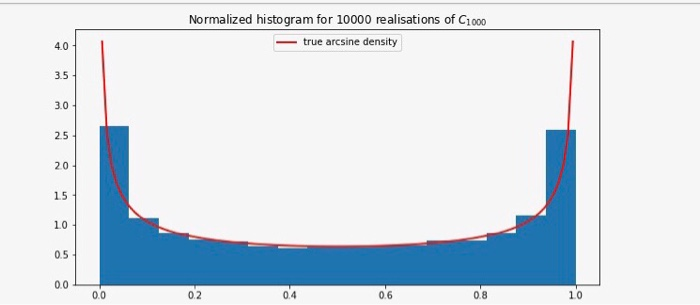
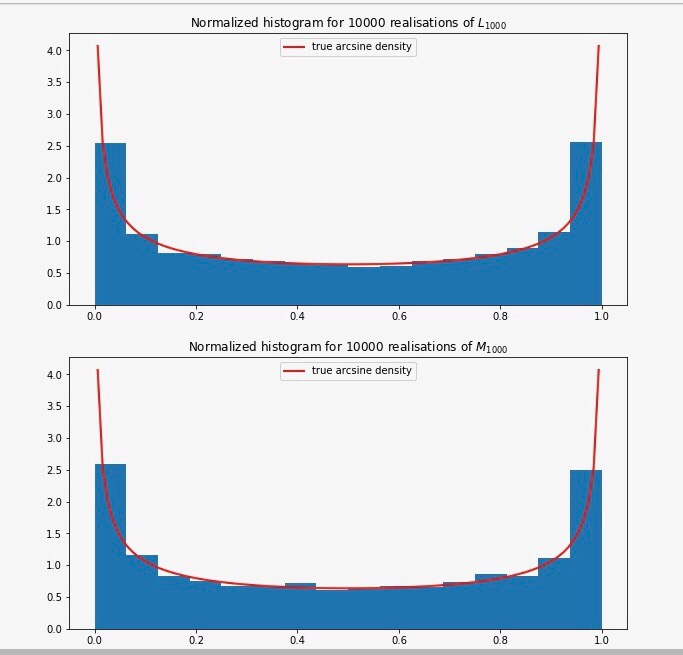
Problem 3 (3 points) Random Walk theory provides us with the following nice (anf maybe counterintuitive) asymptotic statements: lim C2N LA M2v We say that the random variables C2N/2N, L2N/2N, M2N/2N converge in distribution to the Arcsine Distribution. The interesting property about the Arcsine distribution is that its density (see its formula above) is U-shaped on (0, 1). In other words, if X is arcsine-distributed on (0, 1), the probabilty that X takes very small values near 0 or very large values near 1 is rather high, but the probability for taking values around, say, 0.5, is low. [11x np.Linspace(arcsine.ppf(8.05), arcsine.ppf (0.95), 188) plt.title("Density of the arcsine distribution") plt.plot(x, arcsine.pdf(x), linewidth-2, color-'b) Problem 3 (3 points) Random Walk theory provides us with the following nice (anf maybe counterintuitive) asymptotic statements: lim C2N LA M2v We say that the random variables C2N/2N, L2N/2N, M2N/2N converge in distribution to the Arcsine Distribution. The interesting property about the Arcsine distribution is that its density (see its formula above) is U-shaped on (0, 1). In other words, if X is arcsine-distributed on (0, 1), the probabilty that X takes very small values near 0 or very large values near 1 is rather high, but the probability for taking values around, say, 0.5, is low. [11x np.Linspace(arcsine.ppf(8.05), arcsine.ppf (0.95), 188) plt.title("Density of the arcsine distribution") plt.plot(x, arcsine.pdf(x), linewidth-2, color-'b)
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


