Question: Using the information from Problem 8-29, assume that the nursing administrator expected 400 patients for flu shots and 1,600 for flu treatment. The medical group
Using the information from Problem 8-29, assume that the nursing administrator expected 400
patients for flu shots and 1,600 for flu treatment. The medical group typically charges $50 for a flu shot
and $80 for treating a flu patient. Actually, the group had 1,200 patients who received flu shots and
1,400 who had the flu and received treatment. On average, it was able to collect $55 per flu shot and
$70 per flu patient. Compute the volume, mix, and price revenue variances. How did things turn out for
the group considering just revenues? How did they turn out from a profit perspective?
Do I have to calculate the total volume before trying to solve the problem? Also, I am going to attach my work from problem 8-29.
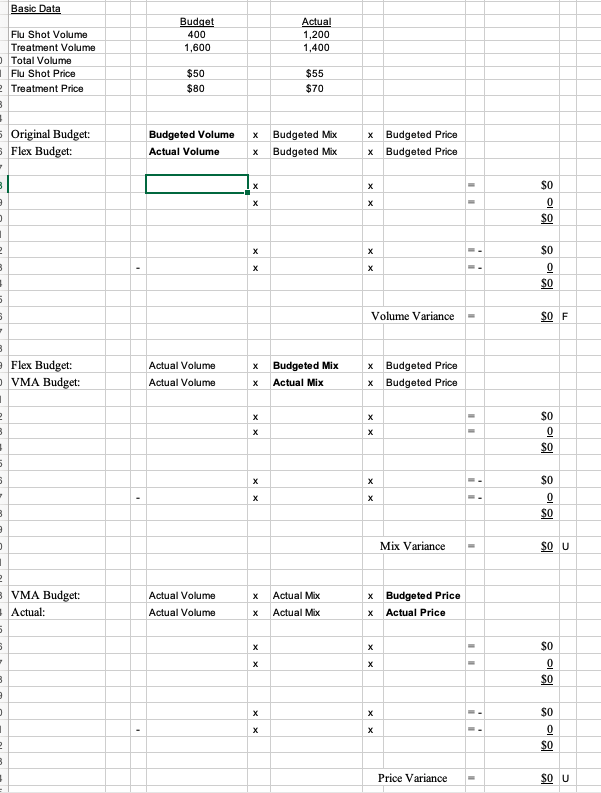
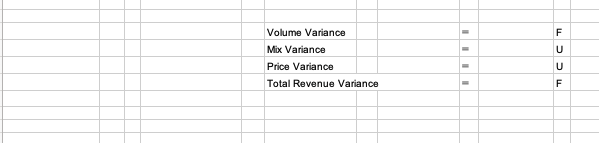

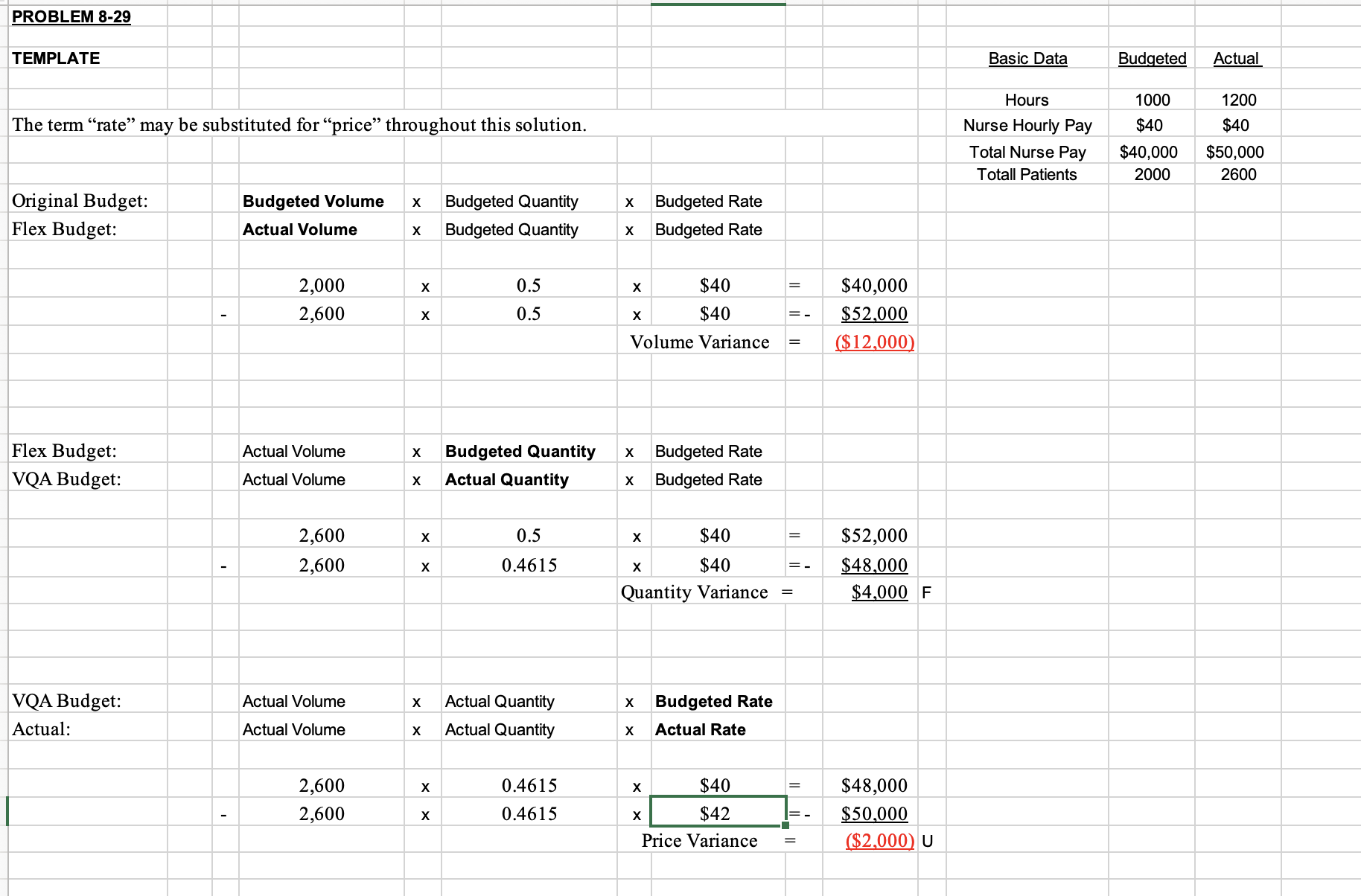
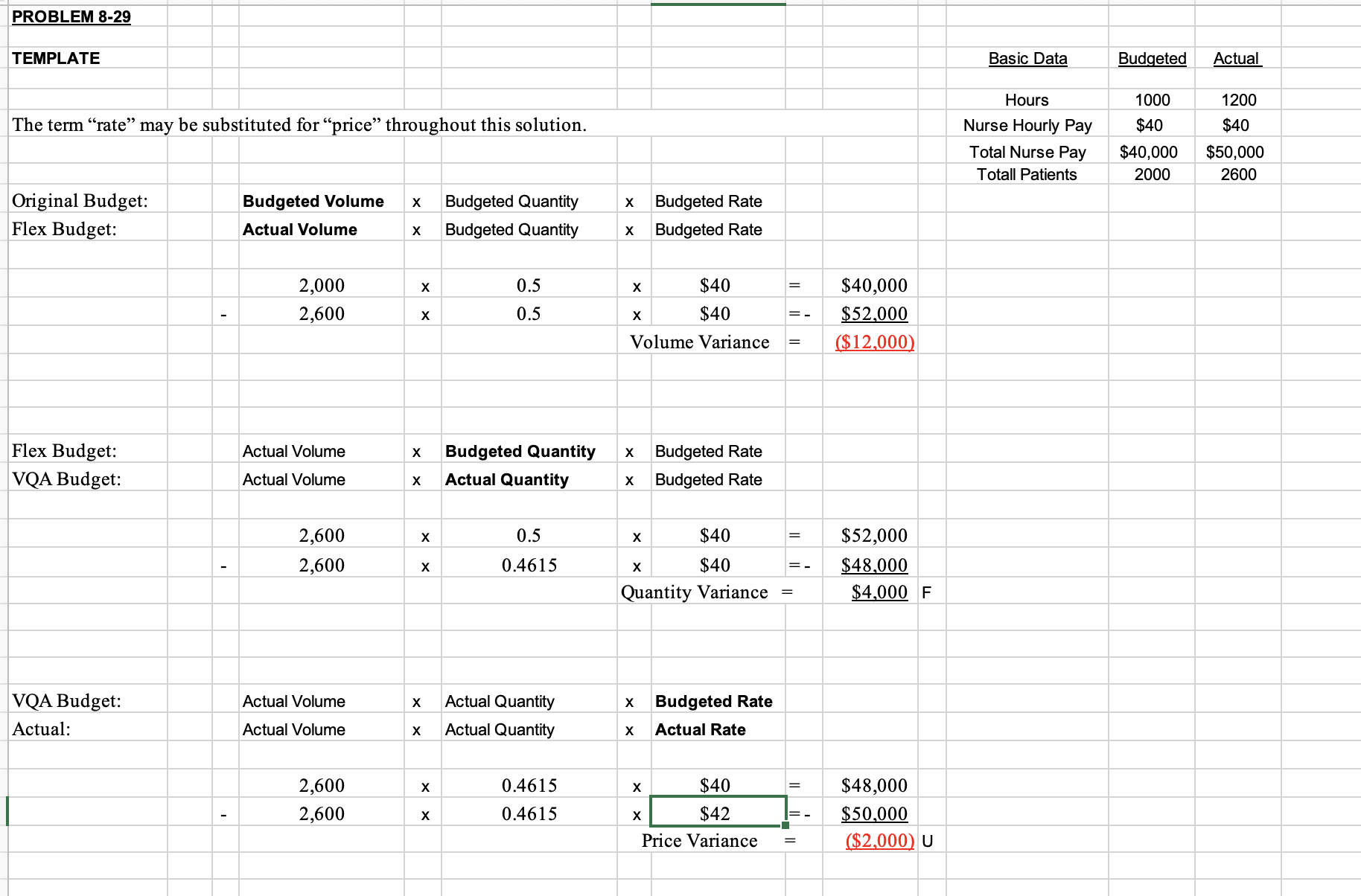
Basic Data Budget Actual Flu Shot Volume 400 1,200 Treatment Volume 1,600 1,400 Total Volume Flu Shot Price $50 $55 Treatment Price $80 $70 Original Budget: Budgeted Volume X Budgeted Mix x Budgeted Price Flex Budget: Actual Volume X Budgeted Mix x Budgeted Price X X SO $0 X X X Volume Variance SO F Flex Budget: Actual Volume X Budgeted Mix x Budgeted Price VMA Budget: Actual Volume X Actual Mix x Budgeted Price X X SO X X $0 Mix Variance SO U VMA Budget: Actual Volume X Actual Mix x Budgeted Price Actual: Actual Volume X Actual Mix x Actual Price X X $0 So X X X $0 Price Variance SO UVolume Variance F Mix Variance U Price Variance U Total Revenue Variance F829. Assume that you are the nursing administrator for a medical group that expects a severe outbreak 417 of u this winter. You hire additional staff to treat patients and administer shots. Your special project budget was for 1,000 hours of parttime nurses' services at $40 per hour, for a total cost of $40,000. It was expected that these nurses would treat 2,000 patients. After the u season was over, it turned out that the total spent on parttime nurses was $50,000. The nurses worked 1,200 hours and 2,600 patients were treated. Calculate the variances. Was the overall result favorable 0r unfavorable? 830. Using the information from Problem 829, assume that the nursing administrator expected 400 patients for u shots and 1,600 for u treatment. The medical group typically charges $50 for a u shot and $80 for treating a u patient. Actually, the group had 1,200 patients who received u shots and 1,400 who had the u and received treatment. On average, it was able to collect $55 per u shot and $70 per u patient. Compute the volume, mix, and price revenue variances. How did things turn out for the group considering just revenues? How did they turn out from a profit perspective?| PROBLEM 8-29 TEM PLATE The term \"rate\" may be substituted for \"price\" throughout this solution. Original Budget: Budgeted Volume x Budgeted Quantity Flex Budget: Actual Volume x Budgeted Quantity 2,000 x 0.5 - 2,600 x 0.5 Flex Budget: Actual Volume x Budgeted Quantity VQA Budget: Actual Volume x Actual Quantity 2,600 x 0.5 - 2,600 x 0.4615 VQA Budget: Actual Volume x Actual Quantity Actual: Actual Volume x Actual Quantity 2,600 x 0.4615 2,600 x 0.4615 x Budgeted Rate x Budgeted Rate x $40 x $40 Volume Variance x Budgeted Rate x Budgeted Rate x $40 x $40 Quantity Variance = x Budgeted Rate x Actual Rate x $40 x I $42 Ii Price Variance = $40,000 $52 000 [$ 12 000! $52,000 $48,000 $4 000 F $48,000 $50,000 [$2 000) U Basic Data Hours Nurse Hourly Pay Total Nurse Pay Totall Patients Budgeted 1000 $40 $40,000 2000 Actual 1200 $40 $50,000 2600
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


