Question: v Part A The Arrhenius equation shows the relationship between the rate constant k and the temperature T in kelvins and is typically written as
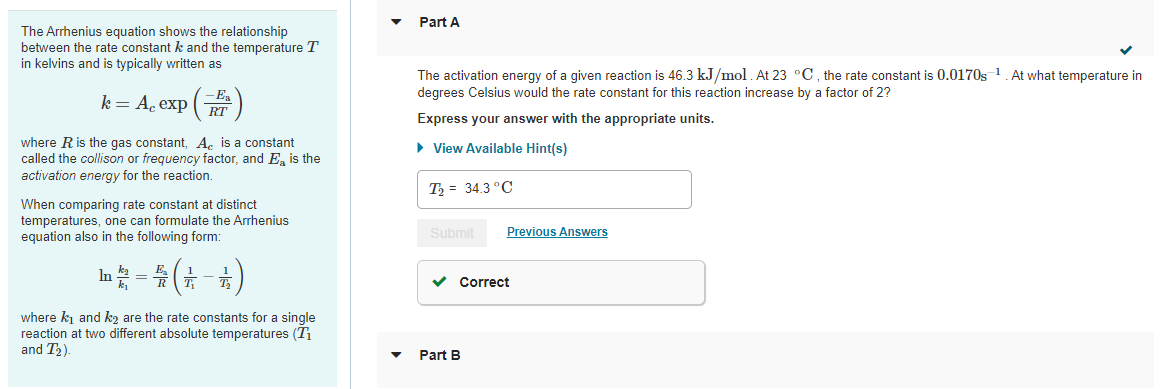
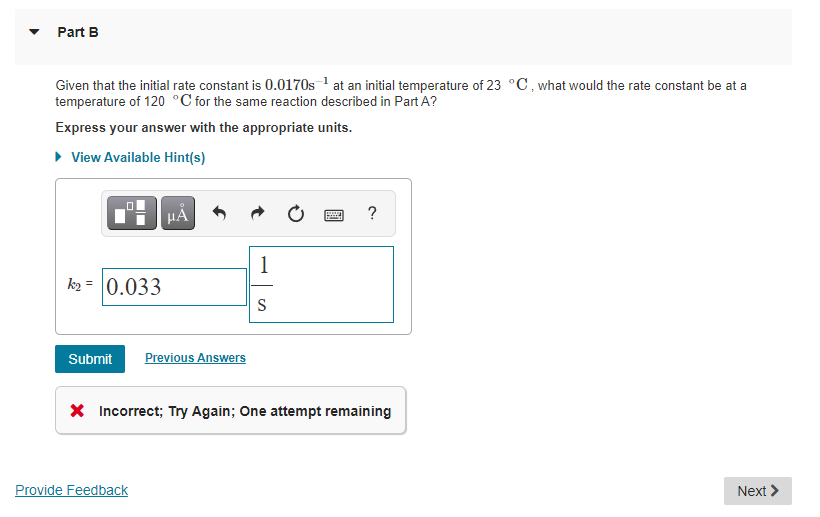
v Part A The Arrhenius equation shows the relationship between the rate constant k and the temperature T in kelvins and is typically written as k= A exp ( -E RT The activation energy of a given reaction is 46.3 kJ/mol At 23 C, the rate constant is 0.0170s-1 At what temperature in degrees Celsius would the rate constant for this reaction increase by a factor of 2? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) where R is the gas constant, Ac is a constant called the collison or frequency factor, and E. is the activation energy for the reaction. When comparing rate constant at distinct temperatures, one can formulate the Arrhenius equation also in the following form: T = 34.3 C Submit Previous Answers = (+) Correct where kj and k2 are the rate constants for a single reaction at two different absolute temperatures (Ti and T2) Part B Part B Given that the initial rate constant is 0.0170s at an initial temperature of 23 C, what would the rate constant be at a temperature of 120 C for the same reaction described in Part A? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s) JO ? 1 k2 = 0.033 S Submit Previous Answers X Incorrect; Try Again; One attempt remaining Provide Feedback Next >
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


