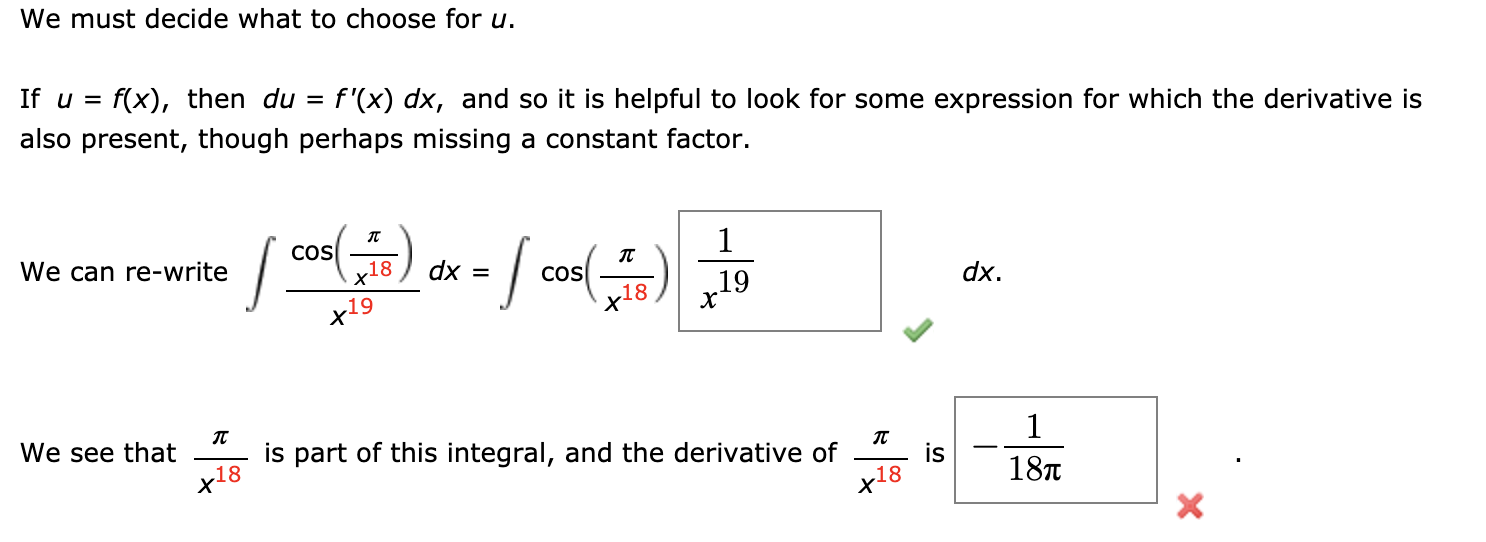
Question: We must decide what to choose for u. If u = f(x), then du = f '(x) dx, and so it is helpful to look
We must decide what to choose for u. If u = f(x), then du = f '(x) dx, and so it is helpful to look for some . . X2 expreSSIon In 1 + x5 dx for which the derivative is also present, though perhaps missing a constant factor. Finding u in this integral is a little trickier than in some others. We see that 1 + x6 is part of this integral, but the derivative of 1 + x6 is |:| , which is not present in the integrand. However, notice that the x2 in the numerator is close to the derivative of x3, which is |:| . We must decide what to choose for u. If u = f(x), then du = f'(x) dx, and so it is helpful to look for some expression in (In (x) ) 47 X dx = (In(x)) 471 dx for which the derivative is also present, though perhaps missing a constant factor. For example, In(x) is part of this integral, and the derivative of In(x) is In(x) 48 48 + C , which is also present. XWe must decide what to choose for u. If u = f(x), then du = f'(x) dx, and so it is helpful to look for some expression for which the derivative is also present, though perhaps missing a constant factor. We can re-write COS 18 dx 1 cos 18 X 19 dx. X19 We see that is part of this integral, and the derivative of 1 is x18 X18 X
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts