Question: What would be the step by step solutions be for these? What is rewritten is the correction. The second picture is the chart we were


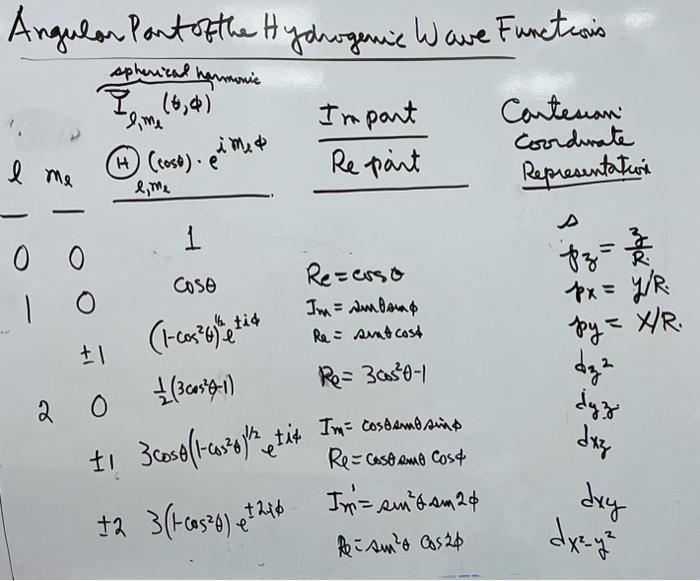
2. Below is a list of spherical harmonics, Y(,) which are used to represent the angular dependence of the electron wave function in a hydrogen atom, as well as the electron wave functions in atoms of higher atomic number. The angle arguments, and , in Ylm(,), are the spherical polar angles. Consider a sphere of unit radius, so that the corresponding Cartesian coordinates are z=cos , x=sincos and y=sinsin. For each of the Ylm(,) listed below, separate the real and imaginary parts, where they occur, and identify the corresponding Cartesian electron orbital that is generated. As a guide, cases (a) and (b) list the Cartesian orbitals corresponding to the p-states. (a) =1,m=0,Y10(,)=cos. Because =1, this is a p-orbital. Because z=cos, it corresponds to a pz - orbital in Cartesian form. (b) =1,m=1,Y11(,)=3cossine. Because =1, and m=1, this Y11(,) generates two p-orbitals. Re[Y11(,)]=3sincos, corresponds to a px - orbital Im[Y11(,)]=3sinsin, corresponds to a py - orbital (c) The following Ym(,) generate the d-orbitals, dz2,dxzdxy,dyz, and dx2y2. Below in Eqs.(1) - (3) are the spherical harmonics corresponding to =2 Y20(,)=21(3cos21)Y21(,)=cossineiY22(,)=sin2e2i Identify which of the Y22(,) in Eqs.(1) - (3) is the parent for each Cartesian dorbitals listed above. 2. Below is a list of spherical harmonics, Ym(,) which are used to represent the angular dependence of the electron wave function in a hydrogen atom, as well as the electron wave functions in atoms of higher atomic number. The angle arguments, and , in Yfm(,), are the spherical polar angles. Consider a sphere of unit radius, so that the corresponding Cartesian coordinates are z=cos x=sincos and y=sinsin. For each of the Ymm(,) listed below, separate the real and imaginary parts, where they occur, and identify the corresponding Cartesian electron orbital that is generated. As a guide, cases (a) and (b) list the Cartesian orbitals corresponding to the p-states. (a) =1,m=0,Y10(,)=cos. Because =1, this is a p-orbital. Because z=cos, it corresponds to a pz - orbital in Cartesian form. (b) =1,m=1,Y11(,) sososinge ei. Because =1, and m=1, this Y11(,) generates two p-orbitals. Re[Y11(,)]=3sincos, corresponds to a px - orbital Im[Y11(,)]=3sinsin, corresponds to a py - orbital (c) The following Ym(,) generate the d-orbitals, dy2,dxzdxy,dyz, and dx2y2. Below in Eqs.(1) - (3) are the spherical harmonics corresponding to =2 Y20(,)=21(3cos21)Y21(,)=cossine1Y22(,)=sin2e2i Identify which of the Y22(,) in Eqs.(1) - (3) is the parent for each Cartesian dorbitals listed above. Angulon Pant of the Hydrogenic Wave Functesis
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


