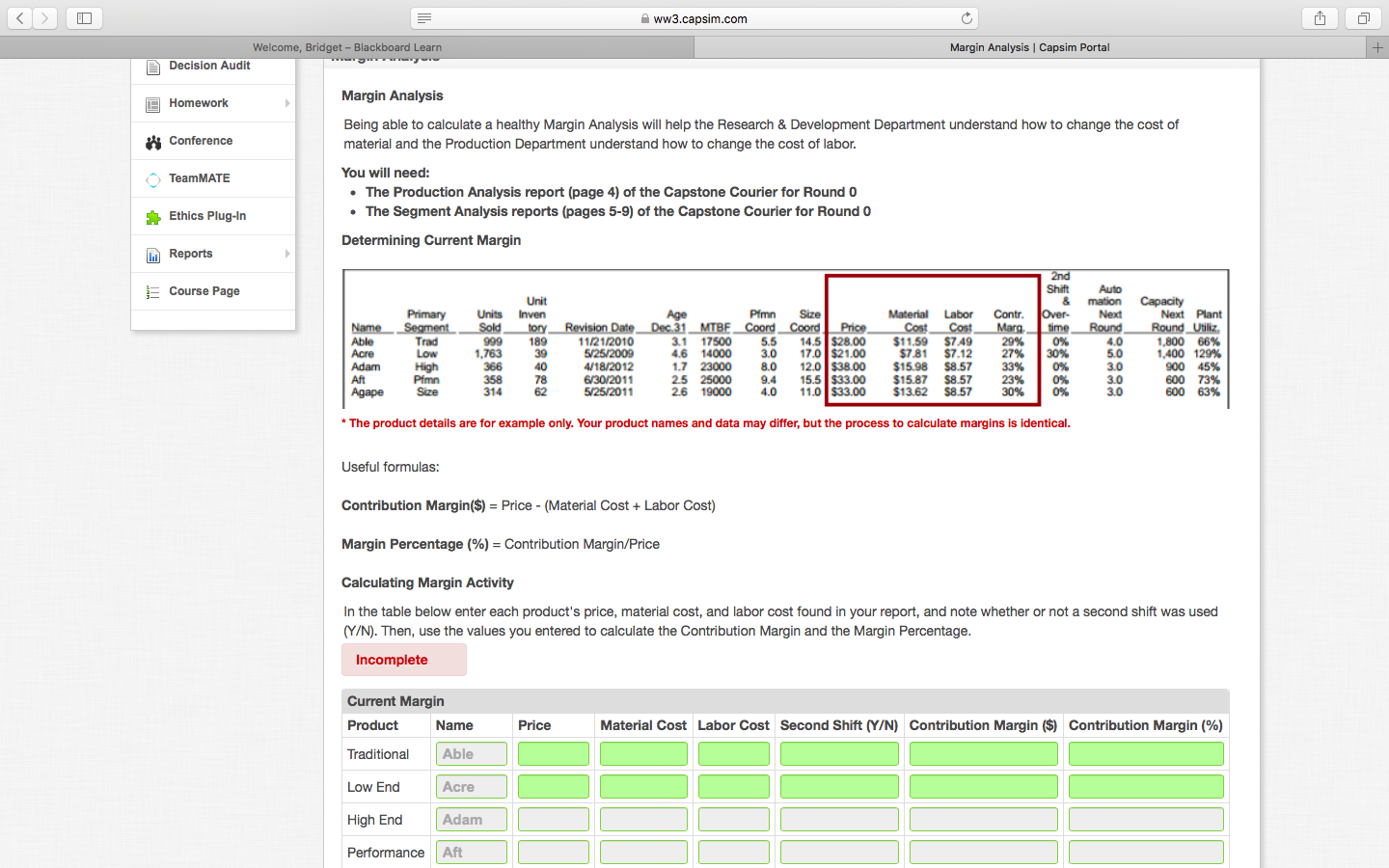
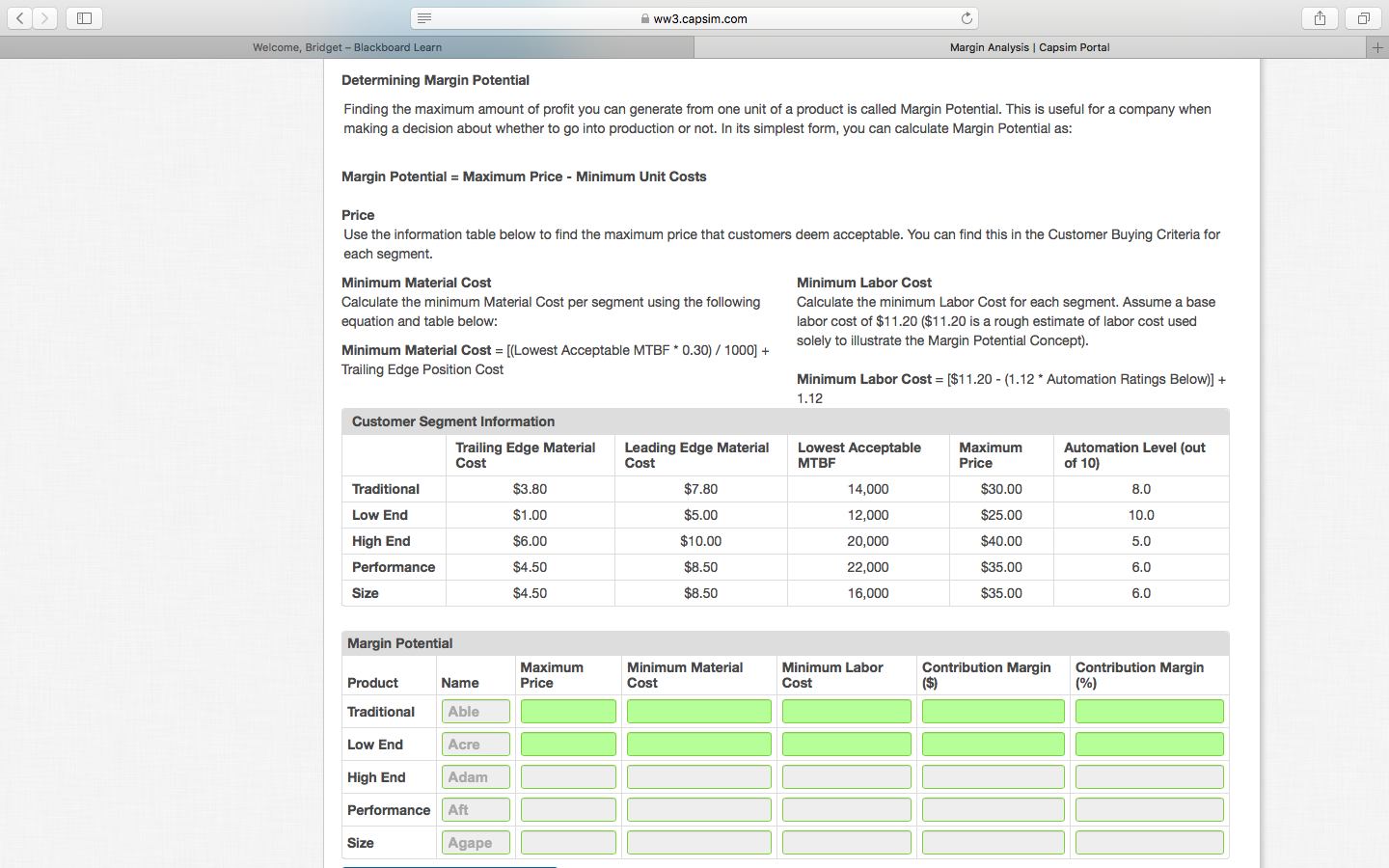
ww3.capsim.com G Margin Analysis Capsim Portal + + Welcome, Bridget - Blackboard Learn wwwwwwwwww Decision Audit A Homework Conference Margin Analysis Being able to calculate a healthy Margin Analysis will help the Research & Development Department understand how to change the cost of material and the Production Department understand how to change the cost of labor. You will need: : The Production Analysis report (page 4) of the Capstone Courier for Round 0 The Segment Analysis reports (pages 5-9) of the Capstone Courier for Round O Determining Current Margin TeamMATE Ethics Plug-In 0 Reports Course Page Name Able Acre Adam Aft Agape 189 Primary Segment Trad Low High Pfmn Size Unit Units inven Age Pimn Size Sold tory_Revision Date_Dec 31 MTBF CoordCoord Price 999 11/21/2010 3.1 17500 5.5 14.5 $28.00 1.763 39 5/25/2009 4.6 14000 3.0 17.0 $21.00 366 40 4/18/2012 1.7 23000 8.0 12.0 $38.00 358 78 6/30/2011 25 25000 9.4 15.5 $33.00 314 62 5/25/2011 26 19000 4.0 11.0 $33.00 Material Labor Cost Cost $11.59 $7.49 $781 $7.12 $15.98 $8.57 $15.87 $8.57 $13.62 $8.57 Contr. Marg, 29% 27% 33% 23% 30% 2nd Shift Auto & & mation Over- Next time_Round 0% 0 4.0 30% 0% 3.0 0% 0% 3.0 5.0 Capacity Next Plant Round Utiliz. 1.800 66% 1,400 129% 900 45% 600 73% 600 63% 3.0 * The product details are for example only. Your product names and data may differ, but the process to calculate margins is identical. Useful formulas: Contribution Margin($) = Price - Material Cost + Labor Cost) Margin Percentage (%) = Contribution Margin/Price Calculating Margin Activity In the table below enter each product's price, material cost, and labor cost found in your report, and note whether or not a second shift was used (Y/N). Then, use the values you entered to calculate the Contribution Margin and the Margin Percentage. Incomplete Current Margin Product Name Price Material Cost Labor Cost Second Shift (Y/N) Contribution Margin ($) Contribution Margin (%) Traditional Able Low End Acre High End Adam Performance Aft ww3.capsim.com G Welcome, Bridget - Blackboard Learn Margin Analysis Capsim Portal + Determining Margin Potential Finding the maximum amount of profit you can generate from one unit of a product is called Margin Potential. This is useful for a company when making a decision about whether to go into production or not. In its simplest form, you can calculate Margin Potential as: Margin Potential = Maximum Price - Minimum Unit Costs Price Use the information table below to find the maximum price that customers deem acceptable. You can find this in the Customer Buying Criteria for each segment. Minimum Material Cost Minimum Labor Cost Calculate the minimum Material Cost per segment using the following Calculate the minimum Labor Cost for each segment. Assume a base equation and table below: labor cost of $11.20 ($11.20 is a rough estimate of labor cost used Minimum Material Cost = [(Lowest Acceptable MTBF* 0.30) / 1000] + solely to illustrate the Margin Potential Concept). Trailing Edge Position Cost Minimum Labor Cost = [$11.20 - (1.12 * Automation Ratings Below)] + 1.12 Customer Segment Information Trailing Edge Material Leading Edge Material Lowest Acceptable Maximum Automation Level (out Cost Cost MTBF Price of 10) Traditional $3.80 $7.80 14,000 $30.00 8.0 Low End $1.00 $5.00 12,000 $25.00 10.0 High End $6.00 $10.00 20,000 $40.00 5.0 Performance $4.50 $8.50 22,000 $35.00 6.0 Size $4.50 $8.50 16,000 $35.00 6.0 Margin Potential Maximum Price Minimum Labor Cost Minimum Material Cost Contribution Margin ($) Product Contribution Margin (%) Name Traditional Able Low End Acre High End Adam Performance Aft Size Agape ww3.capsim.com G Margin Analysis Capsim Portal + + Welcome, Bridget - Blackboard Learn wwwwwwwwww Decision Audit A Homework Conference Margin Analysis Being able to calculate a healthy Margin Analysis will help the Research & Development Department understand how to change the cost of material and the Production Department understand how to change the cost of labor. You will need: : The Production Analysis report (page 4) of the Capstone Courier for Round 0 The Segment Analysis reports (pages 5-9) of the Capstone Courier for Round O Determining Current Margin TeamMATE Ethics Plug-In 0 Reports Course Page Name Able Acre Adam Aft Agape 189 Primary Segment Trad Low High Pfmn Size Unit Units inven Age Pimn Size Sold tory_Revision Date_Dec 31 MTBF CoordCoord Price 999 11/21/2010 3.1 17500 5.5 14.5 $28.00 1.763 39 5/25/2009 4.6 14000 3.0 17.0 $21.00 366 40 4/18/2012 1.7 23000 8.0 12.0 $38.00 358 78 6/30/2011 25 25000 9.4 15.5 $33.00 314 62 5/25/2011 26 19000 4.0 11.0 $33.00 Material Labor Cost Cost $11.59 $7.49 $781 $7.12 $15.98 $8.57 $15.87 $8.57 $13.62 $8.57 Contr. Marg, 29% 27% 33% 23% 30% 2nd Shift Auto & & mation Over- Next time_Round 0% 0 4.0 30% 0% 3.0 0% 0% 3.0 5.0 Capacity Next Plant Round Utiliz. 1.800 66% 1,400 129% 900 45% 600 73% 600 63% 3.0 * The product details are for example only. Your product names and data may differ, but the process to calculate margins is identical. Useful formulas: Contribution Margin($) = Price - Material Cost + Labor Cost) Margin Percentage (%) = Contribution Margin/Price Calculating Margin Activity In the table below enter each product's price, material cost, and labor cost found in your report, and note whether or not a second shift was used (Y/N). Then, use the values you entered to calculate the Contribution Margin and the Margin Percentage. Incomplete Current Margin Product Name Price Material Cost Labor Cost Second Shift (Y/N) Contribution Margin ($) Contribution Margin (%) Traditional Able Low End Acre High End Adam Performance Aft ww3.capsim.com G Welcome, Bridget - Blackboard Learn Margin Analysis Capsim Portal + Determining Margin Potential Finding the maximum amount of profit you can generate from one unit of a product is called Margin Potential. This is useful for a company when making a decision about whether to go into production or not. In its simplest form, you can calculate Margin Potential as: Margin Potential = Maximum Price - Minimum Unit Costs Price Use the information table below to find the maximum price that customers deem acceptable. You can find this in the Customer Buying Criteria for each segment. Minimum Material Cost Minimum Labor Cost Calculate the minimum Material Cost per segment using the following Calculate the minimum Labor Cost for each segment. Assume a base equation and table below: labor cost of $11.20 ($11.20 is a rough estimate of labor cost used Minimum Material Cost = [(Lowest Acceptable MTBF* 0.30) / 1000] + solely to illustrate the Margin Potential Concept). Trailing Edge Position Cost Minimum Labor Cost = [$11.20 - (1.12 * Automation Ratings Below)] + 1.12 Customer Segment Information Trailing Edge Material Leading Edge Material Lowest Acceptable Maximum Automation Level (out Cost Cost MTBF Price of 10) Traditional $3.80 $7.80 14,000 $30.00 8.0 Low End $1.00 $5.00 12,000 $25.00 10.0 High End $6.00 $10.00 20,000 $40.00 5.0 Performance $4.50 $8.50 22,000 $35.00 6.0 Size $4.50 $8.50 16,000 $35.00 6.0 Margin Potential Maximum Price Minimum Labor Cost Minimum Material Cost Contribution Margin ($) Product Contribution Margin (%) Name Traditional Able Low End Acre High End Adam Performance Aft Size Agape






