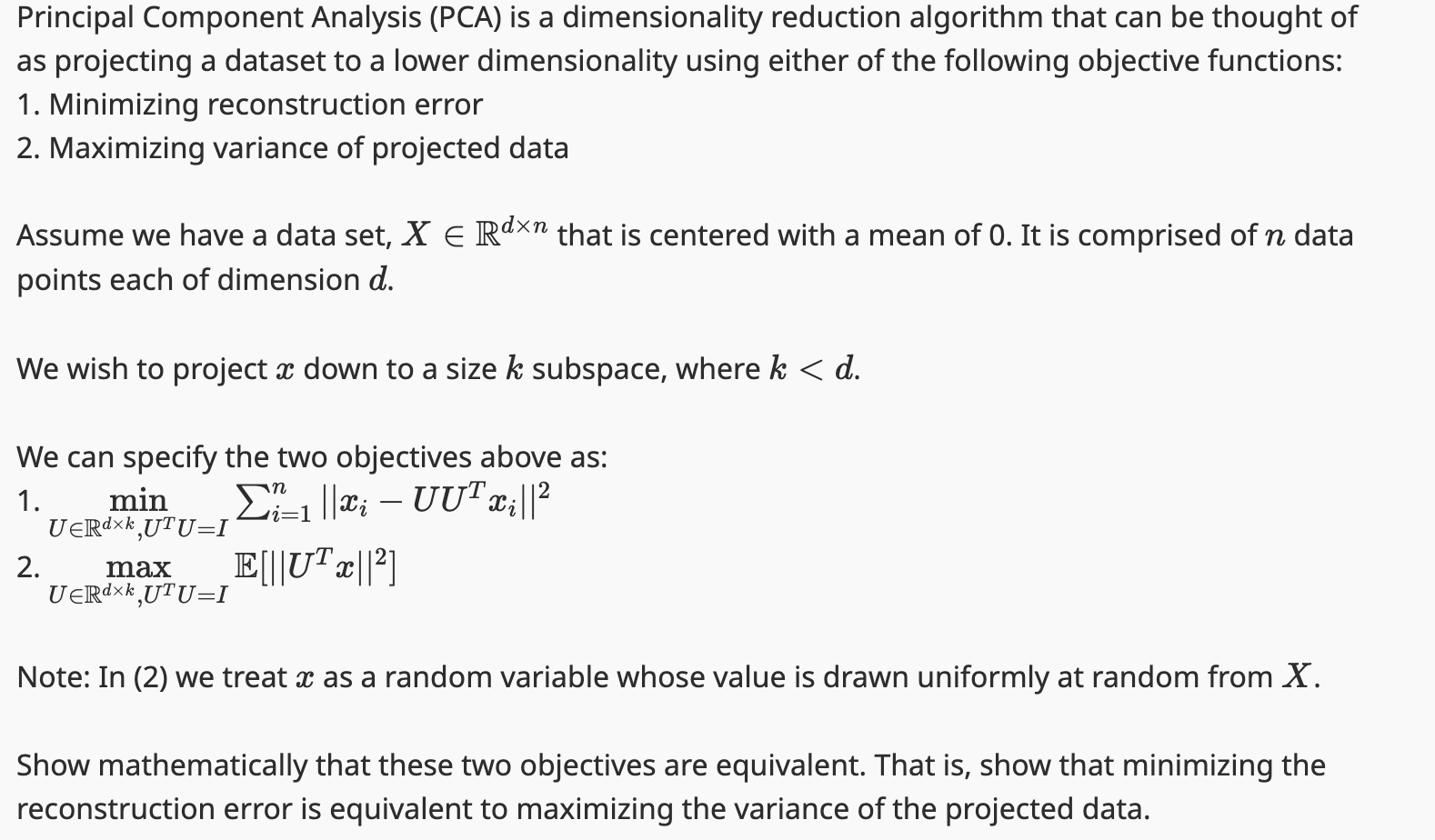
Question: x i n R d n Principal Component Analysis ( PCA ) is a dimensionality reduction algorithm that can be thought of as projecting a
Principal Component Analysis PCA is a dimensionality reduction algorithm that can be thought of as projecting a dataset to a lower dimensionality using either of the following objective functions:
Minimizing reconstruction error
Maximizing variance of projected data
Assume we have a data set, $X in mathbbRd times n$ that is centered with a mean of It is comprised of $n$ data points each of dimension $d$
We wish to project $x$ down to a size $k$ subspace, where $kxinRdtimes n that is centered with a mean of It is comprised of data
points each of dimension
We wish to project down to a size subspace, where
can specify the two objectives above :
Note: treat a random variable whose value drawn uniformly random from
Show mathematically that these two objectives are equivalent. That show that minimizing the
reconstruction error equivalent maximizing the variance the projected data.
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 Expert Approved Answer
Step: 1 Unlock


Question Has Been Solved by an Expert!
Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Step: 2 Unlock
Step: 3 Unlock


