Question: You will create a solution that provides a way of aggregating a set of data. An aggregate function is one that calculates an aggregate value
You will create a solution that provides a way of aggregating a set of data. An aggregate function is one that calculates an aggregate value (e.g. sum, count, average, etc.) from a series of data. The UML diagram below represents a design pattern called a strategy where the strategy is the type of aggregation to apply. It is structurally somewhat similar to the NameFormatter example shown in class where we used interfaces to make a solution extensible by doing callbacks to injected code. In this case, the ValueManager, when asked to get a result, will call back to a supplied aggregation strategy.
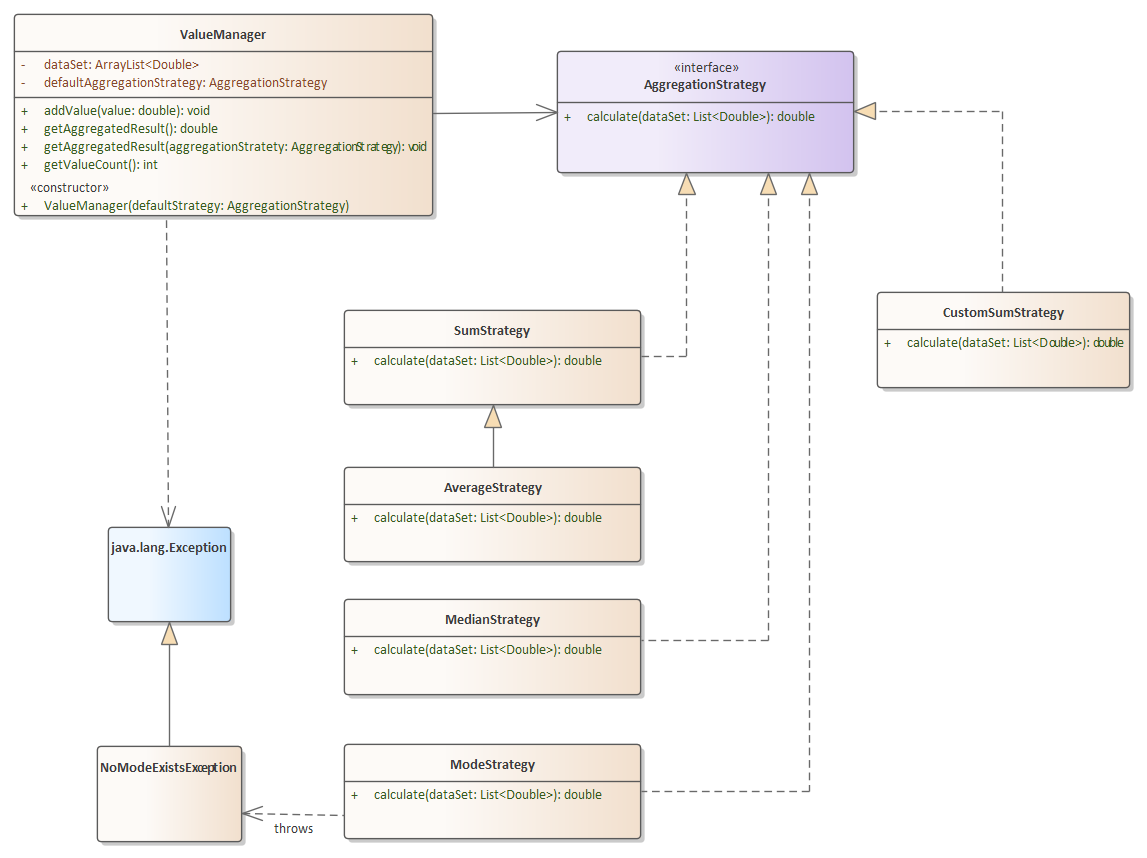
## Classes and Methods
**ValueManager** - Collects data and then produces an aggregated result based upon the strategy provided to its constructor or a provided strategy in the overloaded get
- ValueManager(AggregationStrategy) - constructor that accepts a default AggregationStrategy and stores it
- addValue(value) - adds a the provided value to the dataSet
- getValueCount() - returns the number of items in the dataSet
- getAggregatedResult() - uses its internal AggregrationStrategy provided in constructor to retrieve the aggregrated result. This method is very simple. it just invokes the AggregationStrategy and returns the value
- getAggregatedResult(AggregationStrategy) - overload of no parameter version which accepts a different strategy and uses it instead of the default
**AggregationStrategy** - Interface which requires implementers of to provide a calculate method that returns a result of the appropriate type of aggregation.
**SumStrategy** - calculate(dataset) - Returns the arithmetic sum of the provided set of numbers.
**AverageStrategy** - calculate(dataset) - Returns an arithmetic average of the provided set of numbers. Note from the UML diagram that this class does not *directly* implement AggregationStrategy
**MedianStrategy** - calculate(dataset) - Returns an median value of the provided set of numbers. If the data set size is even, return an average between the two middle-most numbers
**CustomSumStrategy** - calculate(dataset) - Calculates a sum using the logic below
- CustomSumException constructor - Accepts an array of type double. This is called the correlatedDataSet. This should be stored for later use in the calculate method
- calculate - calculates a sum using a custom algorithm
- upon method entry, check that dataSet size is the same as the correlatedDataSet passed to the constructor. Throw an IllegalArgumentException if it doesn't
- Loop through the dataSet using a standard FOR loop. For each loop iteration, get the current value (CV) from the dataSet and the current correlated value (CCV) from the correlatedDataSet. "Current" means the item at the current loop index. Evaluate the loop variable value and the product and quotient of the CV and CCV using the logic table below to determine what to add to the sum if the conditions in the first three columns are true. As you can see, there are 3 possible cases
Evaluate the conditions below and execute the action in the last column. First found condition is executed
| Current Loop Index | op | Product of CV and CCV | op | Quotient of CV and CCV | ACTION: Add to Sum |
| --------------------- | ---- | --------------------- | ---- | ---------------------- | ------------------ |
| Even | AND | (Even | OR | Odd) | CV |
| Evenly divisible by 3 | AND | Odd | AND | Even | CV |
| Otherwise | | | | | 1 |
To read the first row, as an example, if the loop index is even AND (the product of CV and CCV is EVEN **OR** the quotient of CV and CCV is ODD), then add the CV to the sum
ValueManager dataSet: ArrayList
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


