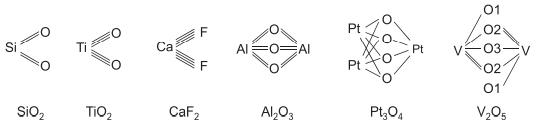
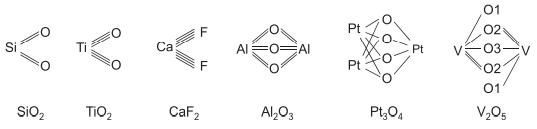
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()


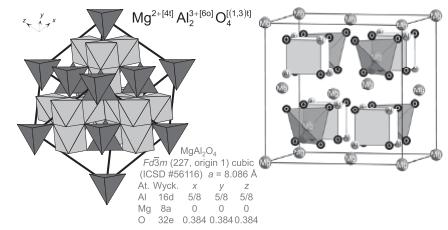
![Mg2+[4] A12+180) Ol(1,3) MgALO Fd3m (227, origin 1) cubic (ICSD # 56116) a= 8.086 A At. Wyck. x Al 16d 5/8](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/images/question_images/1705/6/6/5/28665aa6306b956d1705665286216.jpg)