Question: 2. Perform all the exercises that Peter set for himself. Do you think he should now fully understand MRP? Peter Townsend knew that he would
2. Perform all the exercises that Peter set for himself. Do you think he should now fully understand MRP?
Peter Townsend knew that he would have to make some decisions pretty soon. His sports goods manufacturing business, Psycho Sports, had grown so rapidly over the last 2 years that he would soon have to install some systematic procedures and routines to manage the business. His biggest problem was in manufacturing control. He had started making specialist high-quality table tennis bats, but now made a wide range of sports products, including tennis balls, darts and protective equipment for various games. Furthermore, his customers, once limited to specialist sports shops, now included some of the major sports retail chains.
‘It has taken me nearly two days to get hold of all the information I need. Different people held it, nowhere was it conveniently put together, and sometimes it was not even written down. To get the inventory data, I actually had to go down to the stores and count how many parts were in the boxes’.
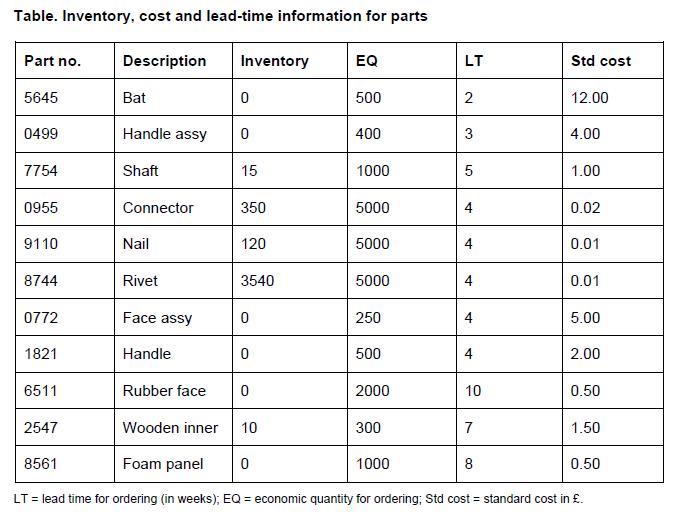
The data Peter collected is as shown in the table below.
Peter set himself six exercises that he knew he would have to master if he was to understand fully the basics of MRP.
Exercise 1 Draw up:
(a) the single-level bill of materials for each level of assembly;
(b) a complete indented bill of materials for all levels of assembly.
Exercise 2
(a) Create the materials requirement planning records for each part and sub-assembly in the bat.
(b) List any problems that the completed MRP records identify.
(c) What alternatives are there that the company could take to solve problems? What are their relative merits?
Exercise 3 On the basis of the first two exercises, create another set of MRP records, this time allowing for a one-week safety lead time for each item, that is, ensuring the items are in stock the week prior to when they are required.
Exercise 4 Over the time period of the exercise, what effect would the imposition of a safety lead time have on average inventory value?
Exercise 5 If we decided that our first task was to reduce inventory costs by 15 per cent, what action would we recommend? What are the implications of our action?
Exercise 6 How might production in our business be smoothed?
Table. Inventory, cost and lead-time information for parts Part no. Description Inventory EQ LT Std cost 5645 Bat 0 500 2 12.00 0499 Handle assy 0 400 3 4.00 7754 Shaft 15 1000 5 1.00 0955 Connector 350 5000 0.02 9110 Nail 120 5000 4 0.01 8744 Rivet 3540 5000 0.01 0772 Face assy 0 250 5.00 1821 Handle 0 500 4 2.00 6511 Rubber face 0 2000 10 0.50 2547 Wooden inner 10 300 7 1.50 8561 Foam panel 0 1000 8 0.50 LT = lead time for ordering (in weeks); EQ = economic quantity for ordering; Std cost = standard cost in .
Step by Step Solution
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


