Question: A onedimensional heat conduction problem can be expressed by the following differential equation: where (k) is the thermal conductivity, (T(x)) is the temperature, and (Q)
A onedimensional heat conduction problem can be expressed by the following differential equation:
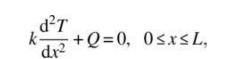
where \(k\) is the thermal conductivity, \(T(x)\) is the temperature, and \(Q\) is heat generated per unit length. \(Q\), the heat generated per unit length, is assumed constant. Two essential boundary conditions are given at both ends: \(T(0)=T(L)=0\). Calculate the approximate temperature \(T(x)\) using the Galerkin method. Compare the approximate solution with the exact one. Hint: Start with an assumed solution in the following form: \(\tilde{T}(x)=c_{0}+c_{1} x+c_{2} x^{2}\), and then make it satisfy the two essential boundary conditions.
dT +Q=0, 0xL, dr
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (150 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To settle the onelayered heat conduction issue utilizing the Galerkin strategy we start by accepting ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


