Two parallel plates are made of two metals 1 and 2 inside a vacuum chamber (Fig. 9.11).
Question:
Two parallel plates are made of two metals 1 and 2 inside a vacuum chamber (Fig. 9.11). The chemical potentials of electrons in metals 1 and 2 are μ1 and μ2. When contact is established between the two metals, conduction electrons flow until equilibrium is reached. As a result of this electron flow, there is a charge Q and −Q at the surface of the electrodes. These electric charges produce an electric field E between the plates. According to relation (9.67) the corresponding electrostatic potential difference Δφ is related to the charge Q by,![]() where C is the capacitance of the capacitor. The plates have a surface area A and theyare separated by a distance d. It can be shown that the capacitance C is given by,
where C is the capacitance of the capacitor. The plates have a surface area A and theyare separated by a distance d. It can be shown that the capacitance C is given by,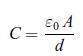
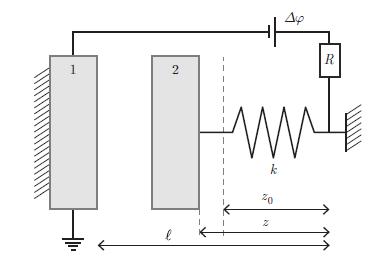 A parallel plate capacitor is made of metals 1 and 2. The metallic plate 1 is fixed mechanically. The metallic plate 2 vibrates under the effect of a spring of elastic constant k.When it vibrates, conduction electrons flow through the resistance R and the spring. The electrostatic potential differenceΔφ is maintained constant by the power supply. where ε0 is the electric permittivity of vacuum. For practical applications, the flow of electric charges is too difficult to detect. It is easier to make the separation distance d oscillate in time, which causes C to vary, hence Q oscillates in time, which implies that an electric current of intensity I flows through the resistance R. Determine the voltage V detected between the plates as a function of d˙, μ1 and μ2.
A parallel plate capacitor is made of metals 1 and 2. The metallic plate 1 is fixed mechanically. The metallic plate 2 vibrates under the effect of a spring of elastic constant k.When it vibrates, conduction electrons flow through the resistance R and the spring. The electrostatic potential differenceΔφ is maintained constant by the power supply. where ε0 is the electric permittivity of vacuum. For practical applications, the flow of electric charges is too difficult to detect. It is easier to make the separation distance d oscillate in time, which causes C to vary, hence Q oscillates in time, which implies that an electric current of intensity I flows through the resistance R. Determine the voltage V detected between the plates as a function of d˙, μ1 and μ2.
Step by Step Answer:

Principles Of Thermodynamics
ISBN: 9781108426091
1st Edition
Authors: Jean-Philippe Ansermet, Sylvain D. Brechet





