Question: Imagine a researcher has taken two random samples from two populations (A and B). Each sample is the same size (N = 71), has the
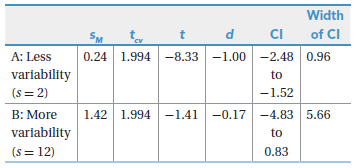
Width CI of CI SM 0.24 1.994 -8.33 -1.00 -2.48 0.96 A: Less variability (s = 2) to -1.52 1.42 1.994-1.41 -0.17 -4.83 5.66 B: More variability (s = 12) to 0.83
Step by Step Solution
3.47 Rating (167 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The less variability there is a The smaller the standard error of ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


