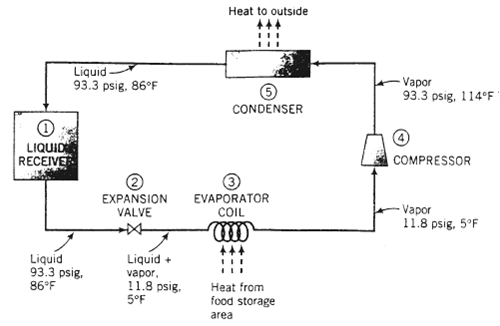
The following diagram shows a simplified version of how a refrigerator works: In a liquid receiver (1),
Question:
The following diagram shows a simplified version of how a refrigerator works: In a liquid receiver (1), a liquid refrigerant (any one of a number of halogenated hydrocarbons such as CC12F2) is contained at high pressure and temperature. The liquid passes through an expansion valve (2), where it flashes to a low pressure. cooling to its boiling point at this pressure and partially evaporating. The liquid?vapor mixture passes though an evaporator coil (3). Air from the food storage area circulates over the coil, and the heat absorbed by the evaporating refrigerant in the coil causes the air to cool. The cold refrigerant vapor emerging from the coil passes to a compressor (4), where it is brought back to a high pressure and in the process is raised to a high temperature. The hot vapor then passes through a condenser (5), where it is cooled and condensed at constant pressure. The air that absorbs the heat given up by the condensing fluid is discharged outside the refrigerator, and the liquefied refrigerant returns to the liquid receiver. Suppose Refrigerant R-12 (the standard name for CCl2F2) undergoes this cycle at a circulation rate of 40lbm/mm, with the temperatures and pressures at the different points of the cycle being those shown on the flow diagram. Thermodynamic data for Refrigerant R-12 are as follows:?
(a) Suppose the expansion valve operates adiabatically and ?Ek is negligible. Use an energy balance about the valve to calculate the fraction of the refrigerant that evaporates in this stage of the process.
(b) Calculate the rate in Btu/min at which heat is transferred to the refrigerant that evaporates in the coil. (This is the useful cooling done in the system.)
(c) If the heat loss in the condenser is 2500 Btu/min, how much horsepower must the compressor deliver to the system? (Use an overall energy balance to solve this problem.)
Step by Step Answer:

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes
ISBN: 978-0471720638
3rd Edition
Authors: Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau





