Question: The geometry of a two-dimensional potential problem is defined in polar coordinates by the surfaces ? = 0, ? = ?, and ?? = a,
The geometry of a two-dimensional potential problem is defined in polar coordinates by the surfaces ? = 0, ? = ?, and ?? = a, as indicated in the sketch.
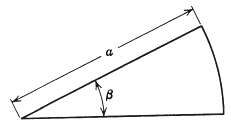
Using separation of variables in polar coordinates, show that the Green function can be written as
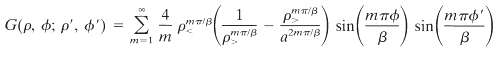
Problem 2.25 may be of use.
22 B DO G(, ; , ') = JE m 1 m mm/B P a sin mad B sin ni'
Step by Step Solution
3.26 Rating (178 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
The Green function G is the solution of the following Poisson equation From the resul... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
44-P-E-E-S (232).docx
120 KBs Word File


