Question: The objective of this problem is to develop thermal models for estimating the steady-state temperature and the transient temperature history of the electrical transformer shown
The objective of this problem is to develop thermal models for estimating the steady-state temperature and the transient temperature history of the electrical transformer shown below.
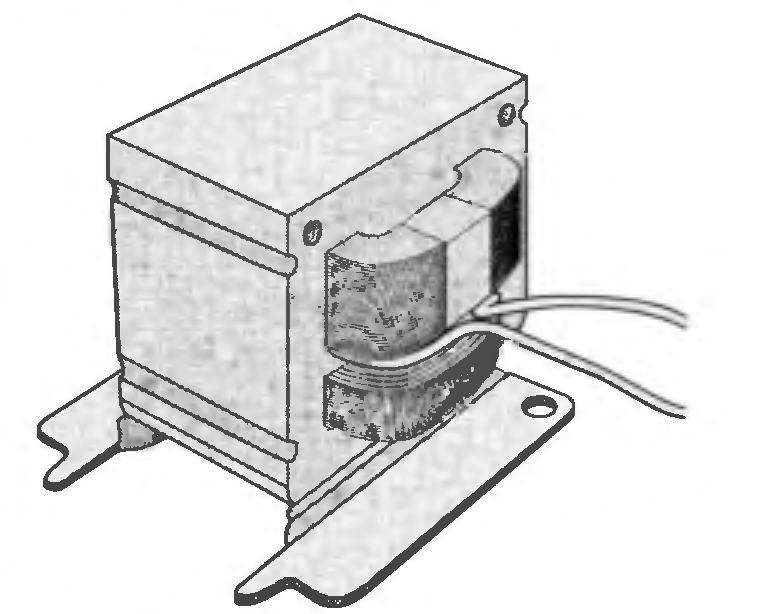
The external transformer geometry is approximately cubical, with a length of 32 mm to a side. The combined mass of the iron and copper in the transformer is 0.28 kg, and its weighted-average specific heat is 400 J/kg ∙ K. The transformer dissipates 4.0 Wand is operating in ambient air at T∞ = 20°C, with a convection coefficient of 10 W/m2 ∙ K. List and justify the assumptions made in your analysis, and discuss limitations of the models.
(a) Beginning with a properly defined control volume, develop a model for estimating the steady-state temperature of the transformer, T (∞). Evaluate T (∞) for the prescribed operating conditions.
(b) Develop a model for estimating the thermal response (temperature history) of the transformer if it is initially at a temperature of Ti = T∝ and power is suddenly applied. Determine the time required for the transformer to come within 5°C of its steady-state operating temperature.
Step by Step Solution
3.31 Rating (181 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
KNOWN Electrical transformer of approximate cubical shape 32 mm to a side dissipates 40 W when opera... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
8-E-M-E-H-M-T (391).docx
120 KBs Word File


