Question: Transmission through thin layers in Figure light is incident perpendicularly on a thin layer of material 2 that lies between (thicker) materials 1 and 3.
Transmission through thin layers in Figure light is incident perpendicularly on a thin layer of material 2 that lies between (thicker) materials 1 and 3. (The rays are tilted only for clarity.) Part of the light ends up in material 3 as ray r3 (the light does not reflect inside material2) and r4 (the light reflects twice inside material 2). The waves of r3 and r4 interfere, and here we consider the type of interference to be either maximum (max) or minimum (min). For this situation, each problem in Table 35-3 refers to the indexes of refraction n1, n2, and n3, the type of interference, the thin-layer thickness L in nanometers, and the wavelength ? in nanometers of the light as measured in air. Where ? is missing, give the wavelength that is in the visible range where L is missing give the second least thickness or the third least thickness as indicated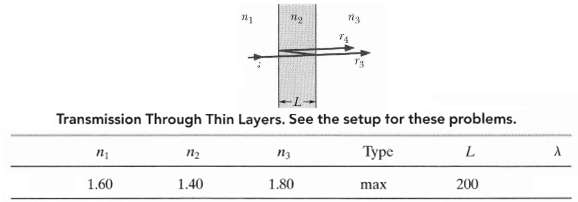
Transmission Through Thin Layers. See the setup tor these problems. , Type 1.80 max 1.60 1.40 200
Step by Step Solution
3.39 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
In t... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
2-P-L-I-L (247).docx
120 KBs Word File


