Question: A two-dimensional potential problem is defined by two straight parallel line charges separated by a distance R with equal and opposite linear charge densities ?
A two-dimensional potential problem is defined by two straight parallel line charges separated by a distance R with equal and opposite linear charge densities ? and ? ?.
(a) Show by direct construction that the surface of constant potential V is a circular cylinder (circle in the transverse dimensions) and find the coordinates of the axis of the cylinder and its radius in terms of R, ?, and V.
(b) Use the results of part a to show that the capacitance per unit length ? of two right-circular cylindrical conductors, with radii a and b, separated by a distance d > a + b, is
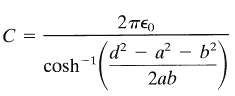
(c) Verify that the result for ? agrees with the answer in Problem 1.7 in the appropriate limit and determine the next nonvanishing order correction in powers of a/d and b/d.
(d) Repeat the calculation of the capacitance per unit length for two cylinders inside each other (d
2 cosh 2ab
Step by Step Solution
3.55 Rating (169 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
a Using known potential for a line char... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
44-P-E-E-S (202).docx
120 KBs Word File


