Question: Electronic devices dissipating electrical power can be cooled by conduction to a heat sink. The lower surface of the sink is cooled, and the spacing
Electronic devices dissipating electrical power can be cooled by conduction to a heat sink. The lower surface of the sink is cooled, and the spacing of the devices ws, the width of the device W d' and the thickness L and thermal conductivity k of the heat sink material each affect the thermal resistance between the device and the cooled surface. The function of the heat sink is to spread the heat dissipated in the device throughout the sink material.
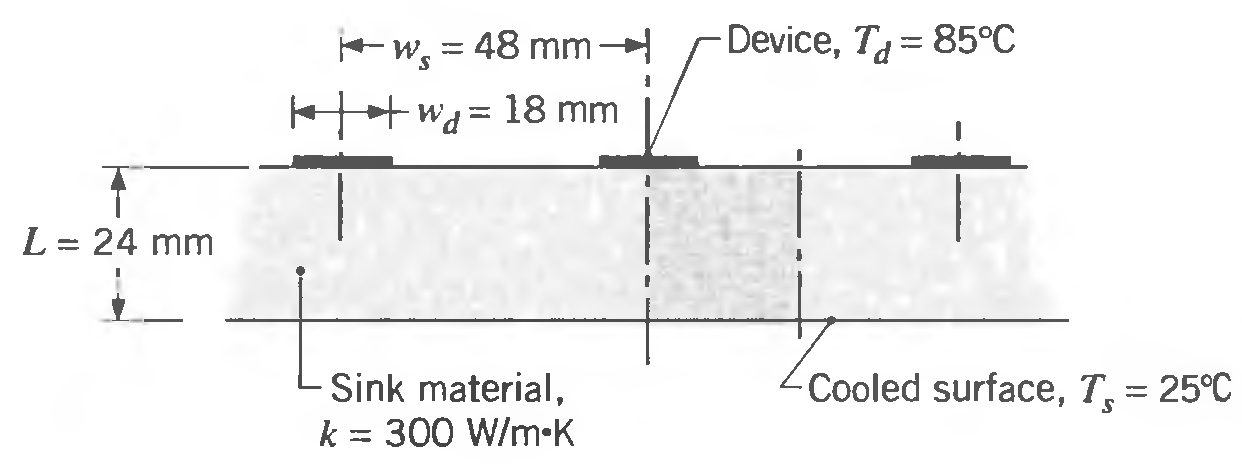
(a) Beginning with the shaded symmetrical element, use a coarse (5 X 5) nodal network to estimate the thermal resistance per unit depth between the device and lower surface of the sink, Rt,d→s (m ∙ K/W). How does this value compare with thermal resistances based on the assumption of one-dimensional conduction in rectangular domains of (i) width Wd and length Land (ii) width W and length L?
(b) Using nodal networks with grid spacing’s three and
five times smaller than that in part (a), determine the effect of grid size on the precision of the thermal resistance calculation.
(c) Using the finer nodal network developed for part
(b), determine the effect of device width on the thermal resistance. Specifically, keeping W s and L fixed, find the thermal resistance for values of wd/ws = 0.175, 0.275, 0.375, and 0.475.
= 48 mm Device, T = 85C +wa= 18 mm L= 24 mm Sink material, k = 300 W/mK -Cooled surface, T, = 25C
Step by Step Solution
3.22 Rating (149 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
KNOWN Electronic device cooled by conduction to a heat sink FIND a Beginning with a symmetrical element find the thermal resistance per unit depth bet... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts
Document Format (1 attachment)
8-E-M-E-H-M-T (354).docx
120 KBs Word File


