Late in 2009, Canyon Power Company (CPC) management was considering expansion of the company's international business activities.
Question:
Late in 2009, Canyon Power Company (CPC) management was considering expansion of the company's international business activities. CPC is an Arizona-based manufacturer of specialist electric motors for use in industrial equipment. All of the company's sales were to other manufacturers in the industrial equipment industry. CPC's worldwide market was supplied from subsidiaries in Germany, Mexico, and Malaysia as well as the United States. The company was particularly successful in Asia, mainly due to the high quality of its products, its technical expertise, excellent after-sale service, and of course the continued rapid economic growth in many Asian countries. This success led corporate management to consider seriously the feasibility of further expansion of its business in the Asian region. The Malaysian subsidiary of CPC distributed and assembled electric motors. It also had limited manufacturing facilities so that it could undertake special adaptations required. With the maturing of the Asian market, particularly in the industrial sector, an expansion of capacity in that market was of strategic importance. The Malaysian subsidiary had been urging corporate management to expand its capacity since the beginning of 2009. However, an alternative scenario appeared more promising. The Indian economy, with its liberalized economic policies, was growing at annual rates much higher than those of many industrialized countries. Further, India had considerably lower labor costs and certain government incentives that were not available in Malaysia. Therefore, the company chose India for its Asian expansion project, and had a four-year investment project proposal prepared by the treasurer's staff. The proposal was to establish a wholly owned subsidiary in India producing electric motors for the Indian domestic market as well as for export to other Asian countries. The initial equity investment would be $1.5 million, equivalent to 67.5 million Indian rupees (Rs) at the exchange rate of Rs 45 to the U.S. dollar. (Assume that the Indian rupee is freely convertible, and there are no restrictions on transfers of foreign exchange out of India.) An additional Rs 27 million would be raised by borrowing from a commercial bank in India at an interest rate of 10 percent per annum. The principal amount of the bank loan would be payable in full at the end of the fourth year. The combined capital would be sufficient to purchase plant of $1.8 million and would cover other initial expenditures, including working capital. The cost of installation would be $15,000, with another $5,000 for testing. No additional working capital would be required during the four-year period. The plant was expected to have a salvage value of Rs 10 million at the end of four years. Straight-line depreciation would be applied to the original cost of the plant.
The firm's overall marginal after-tax cost of capital was about 12 percent. However, because of the higher risks associated with an Indian venture, CPC decided that a 16 percent discount rate would be applied to the project.
Present value factors at 16 percent are as follows:
Period Factor
1 ……………………………. 0.862
2 ……………………………. 0.743
3 ……………………………. 0.641
4 ……………………………. 0.552
Sales forecasts are as follows:
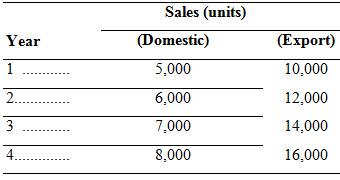
The cash expenditure for operating expenses, excluding interest payments, would be Rs 44 million in Year 1 and was expected to increase at a rate of 8 percent per year. The Indian subsidiary is expected to pay a royalty of Rs 20 million to the parent company at the end of each of the four years. In addition, in those years in which the subsidiary generates a profit, it will pay a dividend to CPC equal to 100 percent of net earnings. Through negotiation with the Indian government, the subsidiary will be exempt from Indian corporate income taxes and withholding taxes on payments made to the parent company. Royalties and dividends received from the Indian subsidiary are fully taxable in the United States at the U.S. corporate tax rate of 35 percent.
Required
Using the information provided, you are required to
a. Calculate net present value from both a project and a parent company perspective.
b. Recommend to CPC corporate management whether or not to accept the proposal.
Net Present ValueWhat is NPV? The net present value is an important tool for capital budgeting decision to assess that an investment in a project is worthwhile or not? The net present value of a project is calculated before taking up the investment decision at... Salvage Value
Salvage value is the estimated book value of an asset after depreciation is complete, based on what a company expects to receive in exchange for the asset at the end of its useful life. As such, an asset’s estimated salvage value is an important... Cost Of Capital
Cost of capital refers to the opportunity cost of making a specific investment . Cost of capital (COC) is the rate of return that a firm must earn on its project investments to maintain its market value and attract funds. COC is the required rate of... Discount Rate
Depending upon the context, the discount rate has two different definitions and usages. First, the discount rate refers to the interest rate charged to the commercial banks and other financial institutions for the loans they take from the Federal... Dividend
A dividend is a distribution of a portion of company’s earnings, decided and managed by the company’s board of directors, and paid to the shareholders. Dividends are given on the shares. It is a token reward paid to the shareholders for their... Exchange Rate
The value of one currency for the purpose of conversion to another. Exchange Rate means on any day, for purposes of determining the Dollar Equivalent of any currency other than Dollars, the rate at which such currency may be exchanged into Dollars...
Step by Step Answer:






