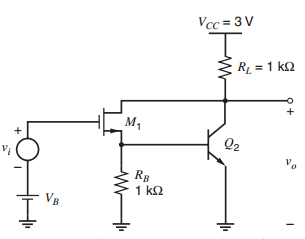
A BiCMOS Darlington is shown in Fig. 3.76. The bias voltage V B is adjusted for a
Question:
Fig. 3.76:
Fantastic news! We've Found the answer you've been seeking!
Step by Step Answer:
Related Book For 

Analysis and Design of Analog Integrated Circuits
ISBN: 978-0470245996
5th edition
Authors: Paul R. Gray, Paul J. Hurst Stephen H. Lewis, Robert G. Meyer
Question Posted:





