Question: In Example 3.7, define quantities (s_{1}=exp left(alpha_{3}+beta_{33} ight)) and (s_{2}=exp left(alpha_{2}+beta_{32} ight)), and by monitoring them obtain the probability that (s_{1}>s_{2}). Data from Example 3.7
In Example 3.7, define quantities \(s_{1}=\exp \left(\alpha_{3}+\beta_{33}\right)\) and \(s_{2}=\exp \left(\alpha_{2}+\beta_{32}\right)\), and by monitoring them obtain the probability that \(s_{1}>s_{2}\).
Data from Example 3.7
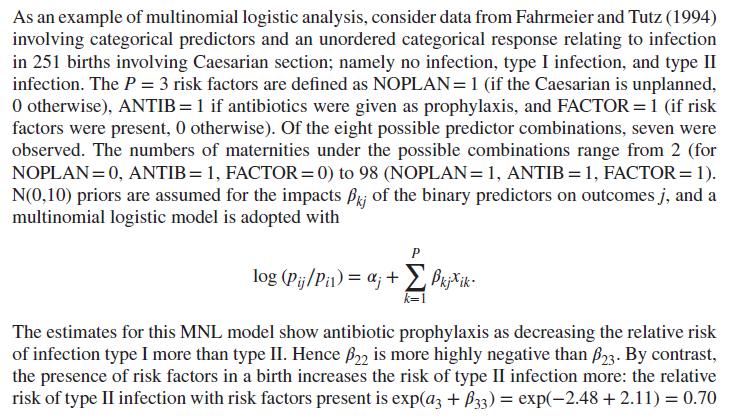
As an example of multinomial logistic analysis, consider data from Fahrmeier and Tutz (1994) involving categorical predictors and an unordered categorical response relating to infection in 251 births involving Caesarian section; namely no infection, type I infection, and type II infection. The P = 3 risk factors are defined as NOPLAN = 1 (if the Caesarian is unplanned, 0 otherwise), ANTIB = 1 if antibiotics were given as prophylaxis, and FACTOR = 1 (if risk factors were present, 0 otherwise). Of the eight possible predictor combinations, seven were observed. The numbers of maternities under the possible combinations range from 2 (for NOPLAN=0, ANTIB = 1, FACTOR = 0) to 98 (NOPLAN = 1, ANTIB = 1, FACTOR = 1). N(0,10) priors are assumed for the impacts Pk of the binary predictors on outcomes j, and a multinomial logistic model is adopted with P log (Pij/Pil) = ; + Pkjxik- k=1 The estimates for this MNL model show antibiotic prophylaxis as decreasing the relative risk of infection type I more than type II. Hence B22 is more highly negative than $23. By contrast, the presence of risk factors in a birth increases the risk of type II infection more: the relative risk of type II infection with risk factors present is exp(a3 + P33) = exp(-2.48 +2.11) = 0.70
Step by Step Solution
3.40 Rating (159 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


