To identify a newly prepared substance, a scientist needs to measure its molar mass. The scientist prepares
Question:
To identify a newly prepared substance, a scientist needs to measure its molar mass. The scientist prepares a solution by dissolving 0.350 g of the unknown compound in 5.42 g ethylene dibromide. This solution has a freezing point of 6.34 °C . Using the data from Example 12.12, find the molar mass of the solute.
Strategy
Use the freezing-point depression to find the number of moles of solute in the sample.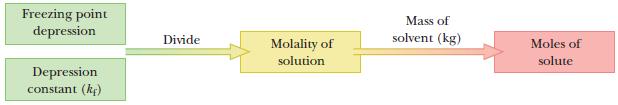
Example 12.12
Pure ethylene dibromide freezes at 9.80 °C . A solution is made by dissolving 0.213 g ferrocene (molecular formula Fe(C5H5)2, molar mass = 186.04 g/mol) in 10.0 g ethylene dibromide. The freezing-point depression constant, kf, for ethylene dibromide is 11.8 °C/molal . What is the freezing point of this solution?
Strategy
To find the freezing point, use Equation 12.5, but first you must calculate the molality of the solution, m. This requires converting the quantity of ferrocene to moles and expressing the quantity of solvent in kilograms. Substitute these quantities into Equation 12.5 and solve for ΔT; then subtract this temperature change from the normal freezing point of ethylene dibromide.
Equation 12.5![]()
Step by Step Answer:

Chemistry Principles And Practice
ISBN: 9780534420123
3rd Edition
Authors: Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball





