The purpose of this problem is to show in three ways that the binding energy of the
Question:
The purpose of this problem is to show in three ways that the binding energy of the electron in a hydrogen atom is negligible compared with the masses of the proton and electron.
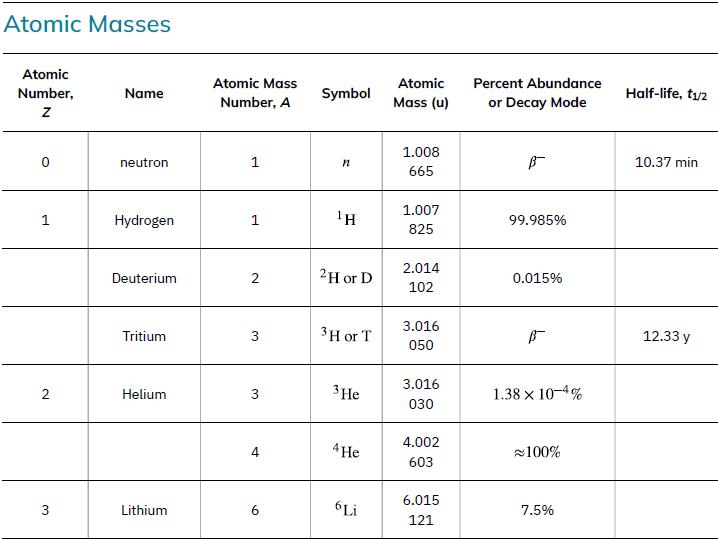
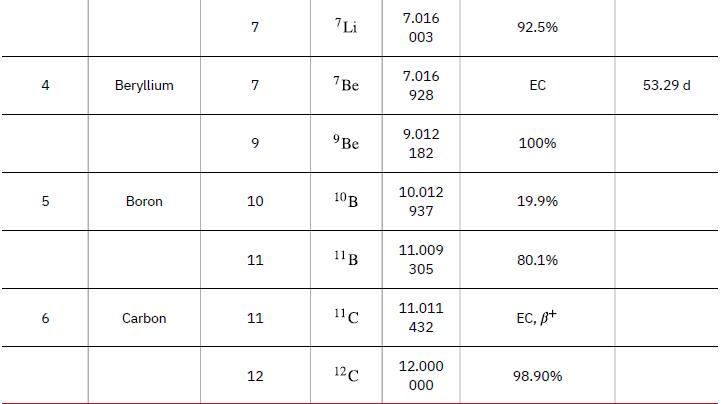
(a) Calculate the mass equivalent in u of the 13.6-eV binding energy of an electron in a hydrogen atom, and compare this with the mass of the hydrogen atom obtained from Appendix a.
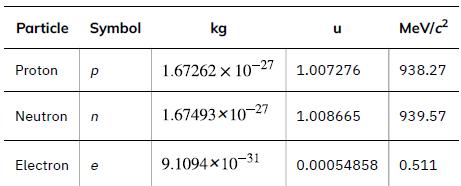
(b) Subtract the mass of the proton given in Table 31.2 from the mass of the hydrogen atom given in Appendix a. You will find the difference is equal to the electron’s mass to three digits, implying the binding energy is small in comparison.
(c) Take the ratio of the binding energy of the electron (13.6 eV) to the energy equivalent of the electron’s mass (0.511 MeV).
Data from Table 31.2
Data from Appendix A.
Step by Step Answer:






