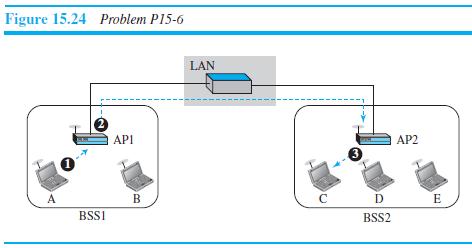
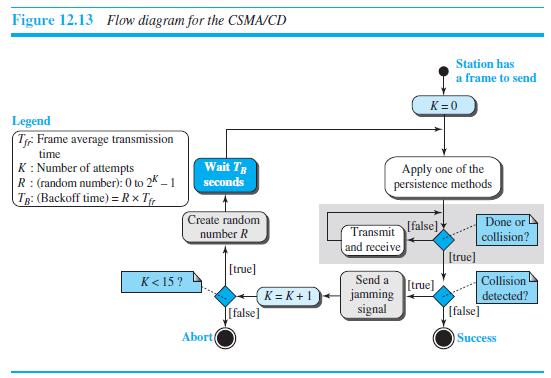
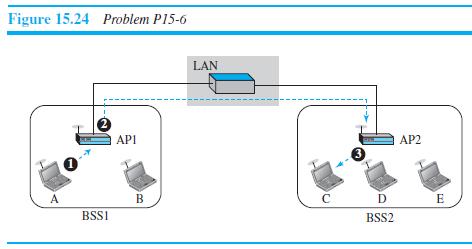
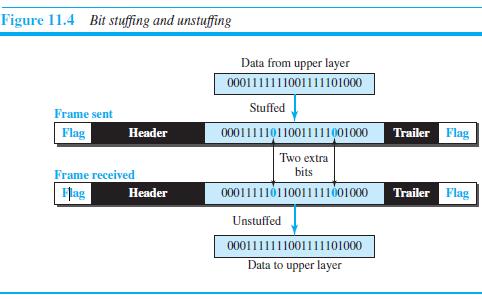
![]()
![]() New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
New Semester Started
Get 50% OFF
Study Help!
--h --m --s
Claim Now
![]()
![]()



![Figure 12.15 Flow diagram of CSMA/CA Station has a frame to send K = 0 Legend K: Number of attempts T: Backoff time IFS: Interframe Space RTS: Request to send CTS: Clear to send Channel free? [false) [true] Carrier sense Wait IFS Choose a random number R between 0 and](https://dsd5zvtm8ll6.cloudfront.net/si.question.images/images/question_images/1607/3/4/6/6795fce29f7e0ef81607346678411.jpg)