Biological pest control has high fixed costs associated with machinery and predator rearing; farmers experience substantial learning
Question:
Biological pest control has high fixed costs associated with machinery and predator rearing; farmers experience substantial “learning by doing”; and farmers also depend on “network externalities”—information gained from fellow farmers and extension agents. Finally, if neighboring farmers are spraying pesticides, the pesticides will also kill off natural predators. Given these factors, assume we can write an average cost function per ton of output for an individual farmer using biological methods that looks like this:

1. Fill in the chart below.
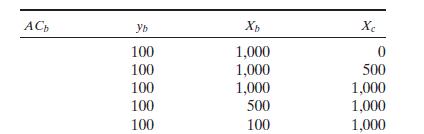
2. Why do the farmer’s costs rise from the top to the bottom of the table (two reasons)?
3. Suppose that chemical-intensive farmers have constant average costs equal to $185 per ton and that prices in this market are driven down to the cost of the lowest cost producer. Define a long-run equilibrium as one in which there is no incentive for entry or exit by one more farmer of either type. Which of the following are long-run equilibria? Of these, which are stable equilibria?
a. Ten biological farmers, each producing 100 tons. No chemical farmers.
b. Ten biological farmers, each producing 100 tons. Five chemical farmers, each producing 100 tons.
c. One biological farmer producing 100 tons. Ten chemical farmers, each producing 100 tons.
d. No biological farmers. Ten chemical farmers, each producing 100 tons.
4. Which of these is the most efficient outcome? If prices fluctuate over time between $200 and the cost of the lowest-cost producer, which will be the likely long-run free-market equilibrium?
5. In the late 1960s, after cotton pests developed pesticide resistance, cotton growers in Texas successfully made a shift to biological pest control methods.
Government infrastructure support (predator rearing, education) was critical in this effort. In Mexico, with no similar support, the cotton industry collapsed.
How could this phenomenon be explained using the cost function above?22
Step by Step Answer:

Economics And The Environment
ISBN: 9781118539729
7th Edition
Authors: Eban S. Goodstein, Stephen Polasky





