Consider the piping system of Fig. P1423, with all the dimensions, parameters, minor loss coefficients, etc., of
Question:
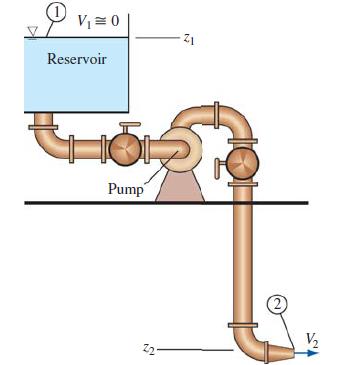
Consider the piping system of Fig. P14–23, with all the dimensions, parameters, minor loss coefficients, etc., of Prob. 14–24. The pump’s performance follows a parabolic curve fit, Havailable = H0 – aV̇2, where H0 = 19.8 m is the pump’s shutoff head, and a 5 0.00426 m/(Lpm)2 is a coefficient of the curve fit. Estimate the operating volume flow rate V̇ in Lpm (liters per minute), and compare with that of Prob. 14–24. Discuss.
Data from Problem 14–24.
Suppose the pump of Fig. P14–23 is operating at free delivery conditions. The pipe, both upstream and downstream of the pump, has an inner diameter of 2.0 cm and nearly zero roughness. The minor loss coefficient associated with the sharp inlet is 0.50, each valve has a minor loss coefficient of 2.4, and each of the three elbows has a minor loss coefficient of 0.90. The contraction at the exit reduces the diameter by a factor of 0.60 (60% of the pipe diameter), and the minor loss coefficient of the contraction is 0.15. Note that this minor loss coefficient is based on the average exit velocity, not the average velocity through the pipe itself. The total length of pipe is 8.75 m, and the elevation difference is (z1 = z2) = 4.6 m. Estimate the volume flow rate through this piping system.
FIGURE P14–23
Step by Step Answer:

Fluid Mechanics Fundamentals And Applications
ISBN: 9780073380322
3rd Edition
Authors: Yunus Cengel, John Cimbala





