In the Are You Wondering 7-1 box, the temperature variation of enthalpy is discussed, and the equation
Question:
In the Are You Wondering 7-1 box, the temperature variation of enthalpy is discussed, and the equation was introduced to show how enthalpy changes with temperature for a constant-pressure process. Strictly speaking, the heat capacity of a substance at constant pressure is the slope of the line representing the variation of enthalpy (H) with temperature, that is

where Cp is the heat capacity of the substance in question. Heat capacity is an extensive quantity and heat capacities are usually quoted as molar heat capacities Cp, m, the heat capacity of one mole of substance, which is an intensive property. The heat capacity at constant pressure is used to estimate the change in enthalpy due to a change in temperature. For infinitesimal changes in temperature,
![]()
To evaluate the change in enthalpy for a particular temperature change, from T1 to T2, we write
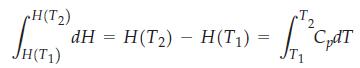
If we assume that Cp is independent of temperature, then we recover equation (7.5)
![]()
On the other hand, we often find that the heat capacity is a function of temperature; a convenient empirical expression is
![]()
What is the change in molar enthalpy of N2 when it is heated from 25.0 °C to 100.0 °C? The molar heat capacity of nitrogen is given by
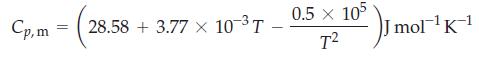
Eq. 7.5
![]()
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette





