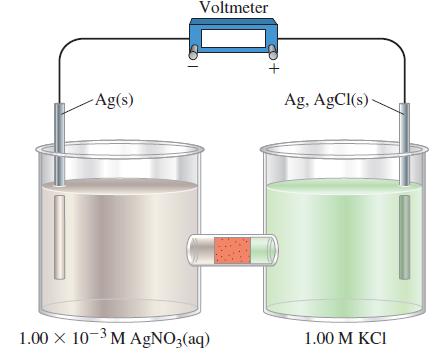
The electrodes in the following electrochemical cell are connected to a voltmeter as shown. The half-cell on
Question:
The electrodes in the following electrochemical cell are connected to a voltmeter as shown. The half-cell on the right contains a standard silver–silver chloride electrode (see Exercise 88). The half-cell on the left contains a silver electrode immersed in 100.0 mL of 1.00 x 10-3 M AgNO3(aq). A porous plug through which ions can migrate separates the half-cells.
(a) What is the initial reading on the voltmeter?
(b) What is the voltmeter reading after 10.00 mL of 0.0100 M K2CrO4 has been added to the half-cell on the left and the mixture has been thoroughly stirred?
(c) What is the voltmeter reading after 10.00 mL of 10.0 M NH3 has been added to the half-cell described in part (b) and the mixture has been thoroughly stirred?
Exercise 88
A common reference electrode consists of a silver wire coated with AgCl(s) and immersed in 1 M KCl.
![]()
(a) What is E°cell when this electrode is a cathode in combination with a standard zinc electrode as an anode?
(b) Cite several reasons why this electrode should be easier to use than a standard hydrogen electrode.
(c) By comparing the potential of this silver–silver chloride electrode with that of the silver–silver ion electrode, determine Ksp for AgCl.
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette





