The extent to which an acid (HA) ionizes in water depends upon the stability of the anion
Question:
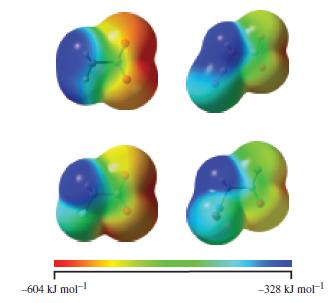
The extent to which an acid (HA) ionizes in water depends upon the stability of the anion (A-); the more stable the anion, the more extensive is the dissociation of the acid. The anion is most stable when the negative charge is distributed over the whole anion rather than localized at one particular atom. Consider the following acids: acetic acid, fluoroacetic acid, cyanoacetic acid, and nitroacetic acid. Draw Lewis structures for their anions, including contributing resonance structures. Rank the acids in order of increasing extent of ionization. Electrostatic potential maps for the four anions are provided on the next page. Identify which map corresponds to which anion, and discuss whether the maps confirm conclusions based on Lewis structures.
Step by Step Answer:

General Chemistry Principles And Modern Applications
ISBN: 9780132931281
11th Edition
Authors: Ralph Petrucci, Jeffry Madura, F. Herring, Carey Bissonnette




