A search engine is designed in such a way to actually find useful information on the World
Question:
A search engine is designed in such a way to actually find useful information on the World Wide Web (WWW) and file transfer protocol (FTP) servers. In technical terms, the search queries and their results show up in the forms of search engine results pages (SERPS) and related information. This information may encompass Web images and other types of useful files. Data mining is also part of this process. In today’s fast-changing global business and MNCs’ diverse operations in domestic and global markets, search engines are highly useful and have been introduced in a multitude of languages. Local cultures and environments matter a lot when designing country-specific search engines.
In global business, data is an important part of search engines. As of 2012, the need for large-scale data is everywhere (consumers and businesses) in global business. The Economist in its annual World in 2012 wrote: “Many more firms will start to analyze huge piles of data to optimize everything from their supply chains to their customer relationships.” Search engines come in different forms and types and may include: general search engines, P2P search engines, meta-search engines, information-specific search engines, geographically based search engines, business search engines, enterprise search engines, and others.
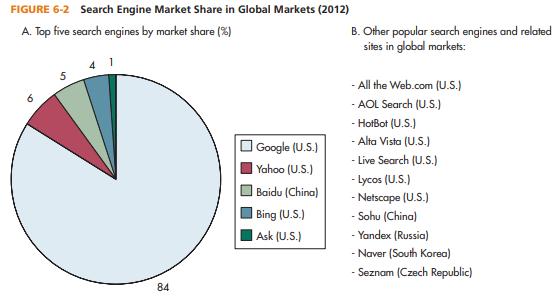
Figure 6-2 provides information on the main search engines in global business. Interestingly, most of the search engines are available worldwide but are based in the U.S. This shows the power of information-related companies that own these search engines. As of 2012, Google is the most popular and powerful search engine in the world, followed by Yahoo, Baidu (China), Bing, and Ask. Of course Google is highly diversified in its products and maintains sites in various languages. This is a perfect reflection of today’s global business with diverse markets and consumers. Google also maintains Google Docs, Google Calendar, Google Site Search, Google Maps, etc. In 2012, Google sales surpassed $37 billion with a market capitalization of $200 billion. This shows the immense power and coverage of this search engine.
Search engines in global business are mostly impacted by local cultures, country-specific data, and national identities. For example, as of 2012, “Baidu” is the largest search engine in China with sales of $2.5 billion, and it carries a market capitalization of $48 billion. “Yandex” is a major search engine in Russia. In addition, South Korea maintains “Naver,” Czech Republic has “Seznam”; “Sohu” is distinctly available in the Chinese market and continues to be a dominant player. Regardless of their types and forms, search engines in global business are highly differentiated on the basis of their functions, country image, and usage. Search engines’ transaction data and search results can reveal an interesting array of data. The search engines and their commercial identity are highly country- and region-specific. No wonder we witness a few search engines that continue to dominate global business. This is also the result of complex value chains where information is commoditized and content specific. In short, search engines such as Google, Yahoo, Baidu, Yandex, Naver, and others will play a major role in their country-specific environments because of business efficiencies and productivity issues. The area is still in its infancy and growth stage and will have massive repercussions for MNCs, domestic companies, governments, and consumers worldwide. Above all, consumers’ privacy and national policies are major variables in the growth of global search engines.
Questions
1. Compare and contrast the top five search engines in global business.
2. Within today’s changing global business, what do you see happening in the next five years regarding search engines’ growth and country-specific issues?
3. Search engines carry national identities and cultures. Compare major search engines from each continent on the basis of their local characteristics and national identities.
Step by Step Answer:

International Management Managing Across Borders And Cultures Text And Cases
ISBN: 9780133062120
8th Edition
Authors: Helen Deresky





