Question: An engineer is measuring a quantity q. It is assumed that there is a random error in each measurement, so the engineer will take n
An engineer is measuring a quantity q. It is assumed that there is a random error in each measurement, so the engineer will take n measurements and reports the average of the measurements as the estimated value of q. Specifically, if Yi is the value that is obtained in the i'th measurement, we assume that Yi = q +Xi, where Xi is the error in the ith measurement. We assume that Xi's are i.i.d. with EXi = 0 and Var(Xi) = 4 units. The engineer reports the average of measurements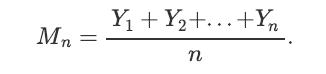
How many measurements does the engineer need to make until he is 95% sure that the final error is less than 0.1 units? In other words, what should the value of n be such that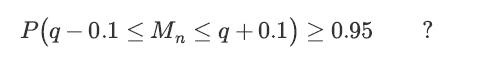
Mn Y+Y+...+Yn n
Step by Step Solution
3.43 Rating (156 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
To find the number of measurements n needed such that the engineer i... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


