The Puxi Company manufactures consumer food products based on soya beans. For convenience purposes the three products
Question:
The Puxi Company manufactures consumer food products based on soya beans. For convenience purposes the three products can be referred to as Alpha (A), Beta (B) and Cappa (C). The production process is relatively simple. In the mixing department, the raw material ingredients are crushed and mixed into a soft paste. This is a machine-intensive rather than labour-intensive process. The ‘paste’ is then transferred to a filling department where the product is bottled, labelled and packaged for distribution. Again, this is a machine-intensive process. Direct labour is a relatively small amount in the overall cost structure. As a result, the company has combined direct labour cost with overhead costs into a ‘conversion cost’ category. In recent months, the manager of Puxi Company has become concerned about various ‘constraints’ facing his company. Perhaps most important was the limited supply of domestically grown soya beans. As a result, the soya beans had to be imported from the US. Unfortunately, most of the soya bean crop grown in the US is genetically modified (GM) and must be tested before use in the EU. The practical implication of this is that the supply of soya beans will be limited for the next financial year. These and other restrictions were discussed at a recent budget meeting of various section managers and are summarized as follows:
1. Supply of soya bean for the next financial year is limited to 500,000 kg, equivalent to a total cost of £500,000.
2. Machine hours availability in the mixing department is restricted to 3,000 hours for the next financial year due to obsolete machinery.
3. Machine hours availability in the filling department is restricted to 2,000 hours for the next financial year due to shortage of machine parts.
4. Contracts had already been signed with various customers to sell a minimum of 10,000 units of each of the three products for the next financial year. These minimum units must be produced and sold.
5. Because no increase or decrease in selling price could be made for the next financial year, the maximum demand for the three products was estimated as follows: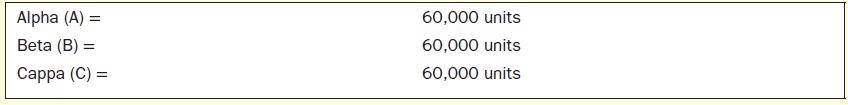
The following information is provided regarding the three products: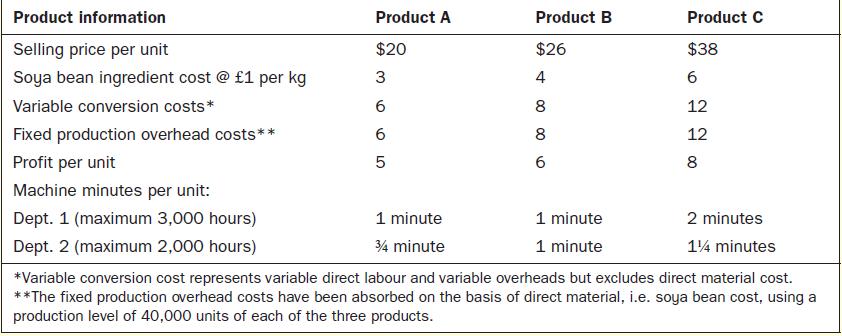
After looking at the information, you quickly present the above data as a linear programming model and solve it using Lindo, that is, a Linear programming software.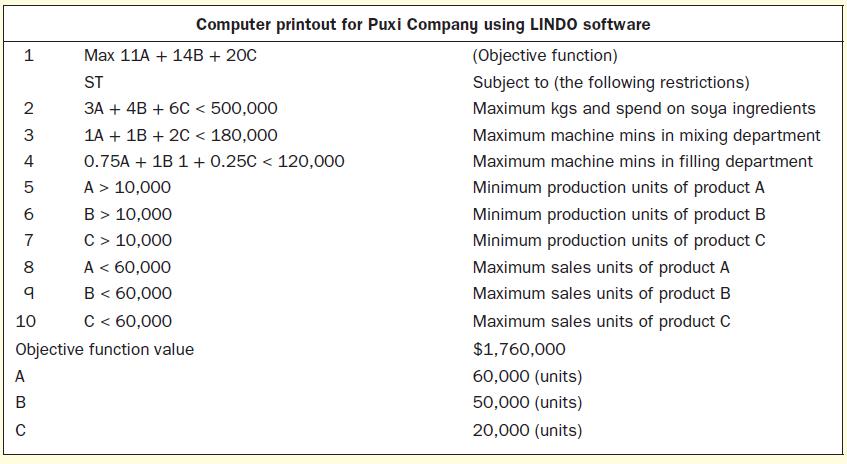
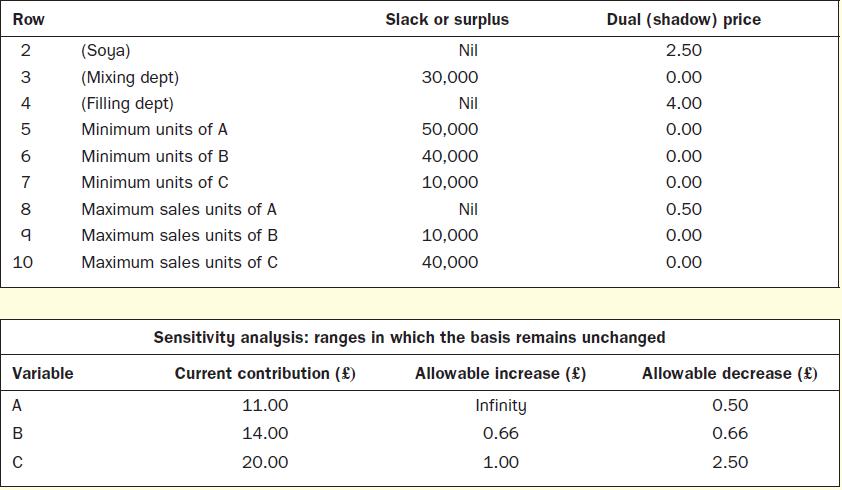
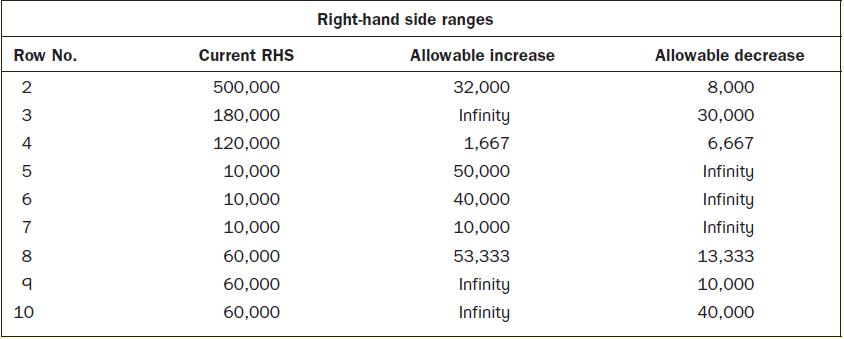
Required
1. Indicate the total revenue, the total contribution (£) generated by the optimal production plan and the physical quantities (units) of each of the three products according to the optimal production plan. Also, indicate the profit for the financial year based on the optimal plan.
2. Calculate the break-even point (BEP) in £ revenue, assuming the constant product mix of the optimal production plan.
3. Clearly identify the impact, if any, on the optimal production plan and on profit of the following independent events:
(a) Selling price of product A increased by £1.
(b) An additional supply of £1,000 worth of soya beans is available.
(c) An additional 1,000 minutes of mixing time becomes available.
(d) An additional 1,000 minutes of filling time becomes available.
4. Identify and explain the opportunity cost, if any, associated with the minimum production of 10,000 units of product A.
5. What is the maximum price that one would pay for one extra kilogram of soya bean ingredient, bearing in mind that each kilogram currently costs £1 per kg? Briefly explain your answer.
6. Briefly explain three limitations associated with using linear programming as a tool of managerial decision making in this manufacturing company.
7. Some manufacturing companies are currently experiencing a shortage of skilled labour. Suggest three ways in which this constraint could be relaxed, where the company employs a combination of skilled and unskilled labour.
Step by Step Answer:

Management Accounting
ISBN: 9780077185534
6th Edition
Authors: Will Seal, Carsten Rohde, Ray Garrison, Eric Noreen





