In Chapter 1, you were given an opportunity to complete the Stroop test, in which color words
Question:
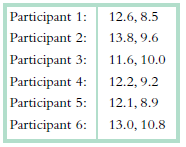
a. What is the independent variable and what are its levels? What is the dependent variable?
b. Conduct all six steps of a paired-samples t test as a two-tailed test. Be sure to label all six steps.
c. Report the statistics as you would in a journal article.
d. Now let€™s look at the effect of switching to a one - tailed test. Conduct steps 2, 4, and 6 of hypothesis testing for a one-tailed paired-samples t test. Under which circumstance€”a one-tailed or a two-tailed test€”is it easier to reject the null hypothesis? If it becomes easier to reject the null hypothesis under one type of test (one-tailed versus two-tailed), does this mean that there is a bigger mean difference between the samples? Explain.
e. Now let€™s look at the effect of p level. Conduct steps 4 and 6 of hypothesis testing for a p level of 0.01 and a two-tailed test. With which p level€” 0.05 or 0.01€”is it easiest to reject the null hypothesis with a two-tailed test? If it is easier to reject the null hypothesis with certain p levels, does this mean that there is a bigger mean difference between the samples? Explain.
f. Now let€™s look at the effect of sample size. Calculate the test statistic using only participants 1€“3 and determine the new critical values. Is this test statistic closer to or farther from the cutoff? Does reducing the sample size make it easier or more difficult to reject the null hypothesis? Explain.
Step by Step Answer:

Essentials Of Statistics For The Behavioral Sciences
ISBN: 9781464107771
3rd Edition
Authors: Susan A. Nolan





