Question: In this exercise we introduce some equivalent formulations of a system of linear equations and then study a linear recursive algorithm for solution of this
In this exercise we introduce some “equivalent” formulations of a system of linear equations and then study a linear recursive algorithm for solution of this system.
Ax = b, A ∈ Rm,n,
1. Consider the system of linear equations where A† is any pseudoinverse of A (that is, a matrix such that AA†A = A). Prove that (7.8) always admits a solution. Show that every solution of equations (7.7) is also a solution for (7.8). Conversely, prove that if b 2 R(A), then every solution to (7.8) is also a solution for (7.7).
![]()
where A† is any pseudoinverse of A (that is, a matrix such that AA†A = A). Prove that (7.8) always admits a solution. Show that every solution of equations (7.7) is also a solution for (7.8). Conversely, prove that if b ∈ R(A), then every solution to (7.8) is also a solution for (7.7).
2. Let R ∈ Rn,m be any matrix such that N(RA) = N(A). Prove that
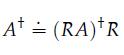
is indeed a pseudoinverse of A.
3. Consider the system of linear equations RAx = Rb,

4. Under the setup of the previous point, consider the following linear iterations: for k = 0, 1, . . .,
![]()

5. Suppose A is positive definite ![]() Discuss how to find a suitable scalar α and matrix R ∈ Rn,n satisfying the conditions of point 3., and such that the iterations (7.10) converge to a solution of (7.9).
Discuss how to find a suitable scalar α and matrix R ∈ Rn,n satisfying the conditions of point 3., and such that the iterations (7.10) converge to a solution of (7.9).
6.

Ax = AAb,
Step by Step Solution
3.42 Rating (155 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
1 We recall18 preliminary that AA is an orthogonal projector onto 18 See RA therefore AA b 2 RA whic... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


