Question: Modify the Scheme program of Figure 11.1 or the OCaml program of Figure 11.3 to simulate an NFA (nondeterministic finite automaton), rather than a DFA.
Modify the Scheme program of Figure 11.1 or the OCaml program of Figure 11.3 to simulate an NFA (nondeterministic finite automaton), rather than a DFA. (The distinction between these automata is described in Section 2.2.1.) Since you cannot “guess” correctly in the face of a multivalued transition function, you will need either to use explicitly coded backtracking to search for an accepting series ofmoves (if there is one), or keep track of all possible states that the machine could be in at a given point in time.
Figure 11.1
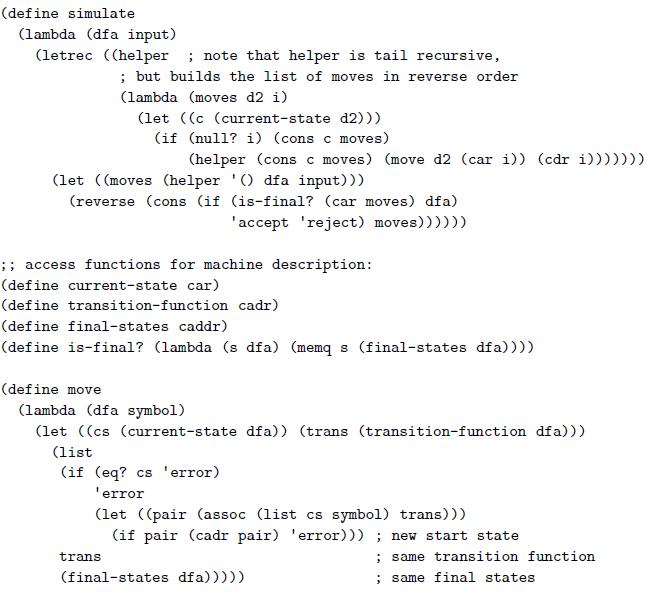
Figure 11.3

(define simulate (lambda (dfa input) (letrec ((helper ; note that helper is tail recursive, ; but builds the list of moves in reverse order (lambda (moves d2 i) (let ((c (current-state d2))) (if (null? i) (cons c moves) (helper (cons c moves) (move d2 (car i)) (cdr i))))))) (let ((moves (helper '() dfa input))) (reverse (cons (if (is-final? (car moves) dfa) 'accept 'reject) moves)))))) ;; access functions for machine description: (define current-state car) (define transition-function cadr) (define final-states caddr) (define is-final? (lambda (s dfa) (mem s (final-states dfa)))) (define move (lambda (dfa symbol) (let ((cs (current-state dfa)) (trans (transition-function dfa))) (list (if (eq? cs 'error) 'error (let ((pair (assoc (list cs symbol) trans))) (if pair (cadr pair) 'error))); new start state trans ; same transition function (final-states dfa))))) same final states
Step by Step Solution
3.58 Rating (165 Votes )
There are 3 Steps involved in it
ANSWER define simulate lambda nfa input letrec helper note that helper is tail recursive but builds ... View full answer

Get step-by-step solutions from verified subject matter experts


